Content
Kinetics: Work and Energy
Energy of the
Position of an Object
Potential
Energy of the Position of an Object
Work and Potential Energy of the Position of an Object
Force of
Gravity and Potential Energy
Gravitational Force and Potential Energy
Spring Force and Potential Energy
Kinetics: Work and Energy
By the introduction of the energy concept, work done on an object by a force through the displacement of the object can also be interpreted using the idea of enegry physically with respect to position.
Energy of the Position of an Object
Work is used to describe some mechanical action acts on an object to change the position of the object. However, the calculated work done on an object can be positive, negative and zero. By the introduction of the kinetic energy idea to describe the motion of an object, the concept of energy can also be used to describe the energy acting on an object with respect to the position of an object. The energy is called potential energy because the energy is meaused with respect to the position of the object. The physical kinetic motion of an object due to the potential energy of the position of an object is used to describe the same mechanical kinetic motion of an object in terms of work. In other words, work is done on an object to over come the potential energy difference of the positions of the object. Besides the energy concept can also be used to explain the sign of work done on an object.
Potential Energy of the Position of an Object
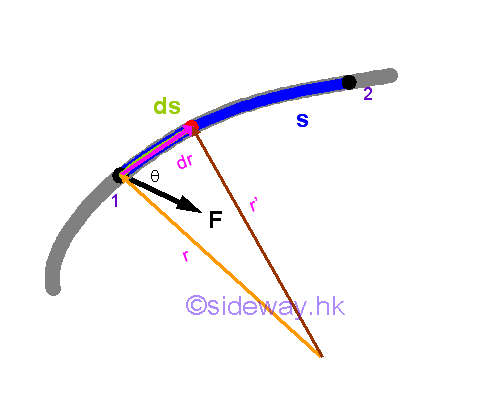
The mechanical action applied to displace an object due to an applied force can be obtained by a dynamic equation of the object through the infinitesimal work done approach. As an infinitesimal work done is used to over come the infinitesimal potential energy difference of the positions of the object, work is equal to the potential energy in magnitude but opposite in sense. And the change of potential energy of the positions of an object due to the work done by the applied force can then be expressed in terms of static quantities, force and static position because the work done by the force is independent of the travelled path.

Assume the indefinite integral of work done on an object be equivilant to the potential energy function of the position of the object. By Newton's third law, whenever there exists force acting upon the object, there always exists a reaction force, which is equal in magnitude but opposite in sense, acting upon the surrounding environment. When considering the pontential energy of the position of the object or the surrounding environment, a corresponging force, that is F'=-F, can be assumed in the function of pontential energy accordingly. Since work is a scalar quantity, potential energy is also a scalar quantity. The potential energy function is a dot product of the force vector and displacement vector, and is a function of position s. Therefore, the potential energy function can be considered as the property of the position of an object with respect to an inertial frame of reference.reference.

Work and Potential Energy of the Position of an Object
As work done on an object can be transformed into the change in potential energy of the position of the object, work of the mechanical motion can be described in terms of the potential energy of the position of the object. Work is negative if the pontential energy increases during the displacement. Work is positive if the pontential energy decreases during the displacement. No work is done if the pontential energy remains unchange.
Force of Gravity and Potential Energy

The force of gravity acts upon an object on earth surface is assumed to be constant when the displacement of the object is small. Since the weight of an object due to the force of gravity consists of only one rectangular component along the vertical direction, the infinitesimal work done by the force of gravity is equal to the weight of the object time the infinitesimal vertical displacement of the object with respect to an inertial frame of reference on earth surface. As the work done by the force of gravity depends only on the initial and final position of the path and is independent of the travelled path, the integral function of work done on an object with respect to the force of gravity can be described as the pontential energy of the object with respect to the position of the object. Imply.

For the pontential energy with respect to the force of gravity, the pontential energy increases linearly from the ground and therefore the potential energy difference with respect to the force of gravity can be expressed as the vertical displacement between two position. Therefore work is negative with respect to the force of gravity if the pontential energy increases during the displacement moving upward. Work is positive with respect to the force of gravity if the pontential energy decreases during the displacement moving downward. No work is done with respect to the force of gravity if the pontential energy remains unchange during the displacement moving horizontally. In other words, work is needed to be done on an object in order to move the object upward under the force of gravity. And an object always drops downward freely under the force of gravity. Although no work is done by the force of gravity to move an object horizontally, force is still needed to act upon the object in order to move the object from rest horizontally according Newton's first law. Therefore work must done by an applied force in order to move the object from rest horizonally under the force of gravity.
Gravitational Force and Potential Energy

For the gravitational force in the planetary motion, the radial gravitational force is a function of radius and can not be assumed to be a constant. Since the centripetal force of an object due to the fgravitational force consists of only one radial component along the radial direction, the infinitesimal work done by the gravitational force is equal to the centripetal force of the object times the infinitesimal radical displacement of the object with respect to an inertial frame of reference on centre of the Earth. As the work done by the centripetal force depends only on the initial and final position of the path and is independent of the travelled path, the integral function of work done on an object with respect to the gravitational force can be described as the pontential energy of the object with respect to the position of the object. Imply.
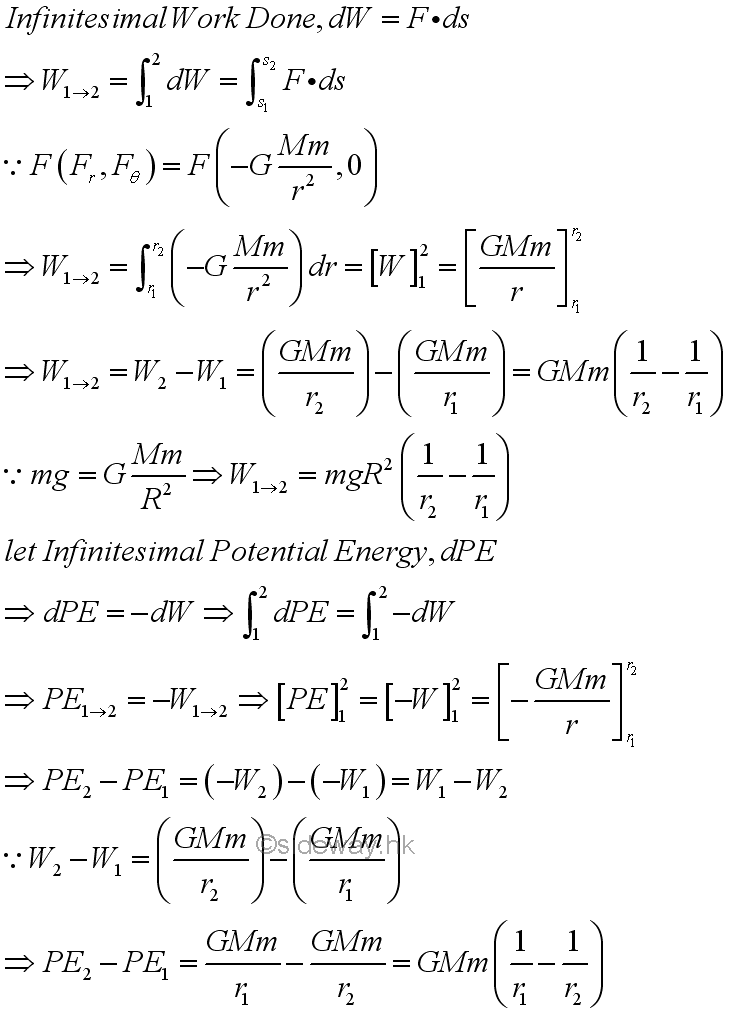
For the pontential energy with respect to the gravitational force, the pontential energy increases inversely proportional to the distance apart because of the negative sense of the gravitational potential energy. When the distance apart tends to infinity, the gravitational potential energy equals to zero. But when two objects get closer together, the gravitational potential energy decreases and is negative in sense. Therefore work is negative with respect to the gravitational force if the pontential energy increases during the displacement of the object moving away from the mass object located on the origin of the initial frame of reference. Work is positive with respect to the gravitational force if the pontential energy decreases during the displacement of the object moving closer to the mass object located on the origin of the initial frame of reference.
For example, an object moves with initial tangential velocity at position A and following a hyperbola, parabola or ellipse orbit, the tangential velocity of the object decreases as the object moving away from the origin O on the upper part of the orbit because negative work is done on the object by the gravitational force to decelerate the motion of the object. While on the lower part of the orbit, the tangential velocity of the object increases as the object moving closer to the origin O because positive work is done on the object by the gravitational force to accelerate the motion of the object.
Spring Force and Potential Energy

For the spring force of an extension spring, the spring force exerted on an object is opposite to the displacement of the object when the spring is extending. Since friction force is ignored, the infinitesimal work done by the spring force is equal to the spring force acting on the object times the infinitesimal linear displacement of the object with respect to an inertial frame of reference. As the work done by the spring force depends only on the initial and final position of the path and is independent of the travelled path, the integral function of work done on an object with respect to the spring force can be described as the pontential energy of the object with respect to the position of the object. Imply.

For the pontential energy with respect to the spring force, the pontential energy increases proportional to the square of distance extended. Therefore work is negative with respect to the spring force if the pontential energy increases during the displacement of the object by stretching the spring from the natural position of the spring on the origin of the initial frame of reference. Work is positive with respect to the spring force if the pontential energy decreases during the displacement of the object by releasing the extended spring to the natural position of the spring on the origin of the initial frame of reference.

Since the spring force depends only upon the initial and final position of the extension of spring with respect to the natural position of the spring, the equations for work done and pontential energy for an extension spring can also be used for a rotating spring with one fixed end.
©sideway
ID: 141100003 Last Updated: 12/4/2014 Revision: 1 Ref:
References
- I.C. Jong; B.G. rogers, 1991, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics
- F.P. Beer; E.R. Johnston,Jr.; E.R. Eisenberg, 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Space(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 35
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
