Content
Wave Reflection inside Enclosures, 1D
Duct, 1D mode, with two closed ends
Duct, 1D mode, with two open ends
Duct, 1D mode, with
one end open and one end closed
Wave Reflection inside Enclosures, 1D
A sound source radiates outwardly in any direction in a free source will always encounter reflecting surfaces unless the sound source is place in an anechoic chamber where all sound energy is almost absorbed with any reflection. And in such case then only wave equation should be satisified without any boundary conditions.
Multiple reflection in an enclosure due to the wall creates standing waves with acoustic modes charactered by frequencies and mode shapes. These modes should satisfied the wave equation and boundary conditions simultaneously.
The boundary conditions are usually defined in terms of continuity between the wall motion and the particle velocity.
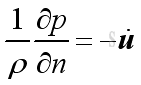
The wall characteristics are usually expressed in term of impedance. A rigid wall is used to describe a wall with higher impedance while a soft wall is used to describe a wall with lower impedance.
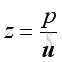
Duct, 1D mode, with two closed ends

The 1D wave equation is
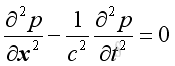
Assume harmonic sound wave imply
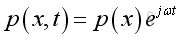
Take the time differential operation, imply
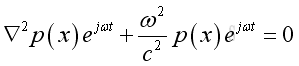
And get the Helmoltz equation,
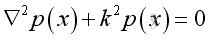
Assume the solution of the equation of the form,
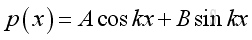
Assume the two closed ends are rigid wall, the boundary conditions at two ends are with particle velocity equals to zero, imply
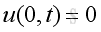 and
and
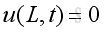
From the equation of momentum conservation
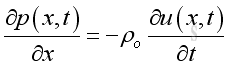
At x = 0 or x=L, u=0, therefore the time derivative of u is zero also, imply:
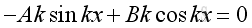
From boundary condition at x=0, imply:
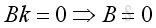
From boundary condition at x=L, imply:
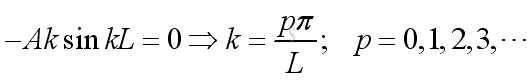
Substitute k, A and B into the pressure function, imply:
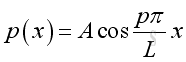 and
and
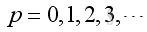
Therefore the natural frequency and mode shape is:
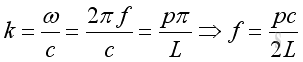 ,
,
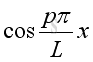 and
and
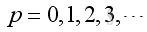
Duct, 1D mode, with two open ends

The 1D wave equation is
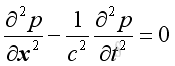
Assume harmonic sound wave imply
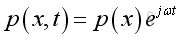
Take the time differential operation, imply
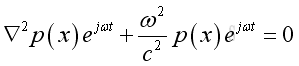
And get the Helmoltz equation,
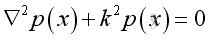
Assume the solution of the equation of the form,
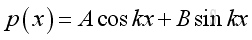
With two open ends, the boundary conditions at two ends are with pressure equals to zero, imply
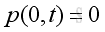 and
and
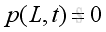
From boundary condition at x=0, imply:
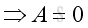
From boundary condition at x=L, imply:
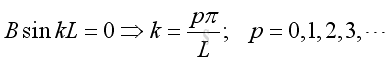
Substitute k, A and B into the pressure function, and p<>0, imply:
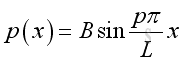 and
and
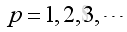
Therefore the natural frequency and mode shape is:
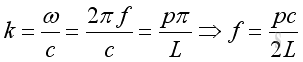 ,
,
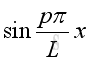 and
and
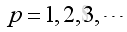
Duct, 1D mode, with one end open and one end closed

The 1D wave equaton is
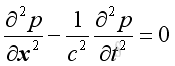
Assume harmonic sound wave imply
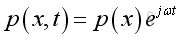
Take the time differential operation, imply
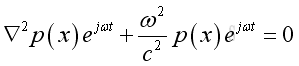
And get the Helmoltz equation,
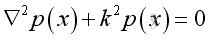
Assume the solution of the equation of the form,
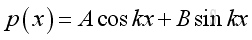
Assume the closed end is rigid wall, the boundary conditions at closed end is with particle velocity equals to zero, imply
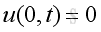
From the equation of momentum conservation
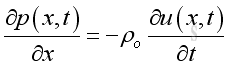
At x = 0, u=0, therefore the time derivative of u is zero also, imply: o, imply:
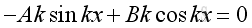
From boundary condition at x=0, imply:
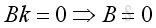
From boundary condition at x=L, imply:
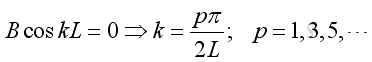
Substitute k, A and B into the pressure function, imply:
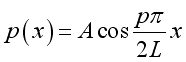 and
and
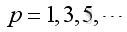
Therefore the natural frequency and mode shape is:
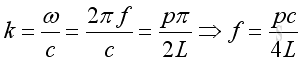 ,
,
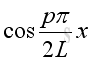 and
and
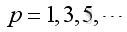
©sideway
ID: 101000021 Last Updated: 10/20/2010 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- Michael P. Norton; Denis G. Karczub,, 2003, Fundamentals of Noise and Vibration Analysis for Engieer
- G. Porges, 1977, Applied Acoustics
- Douglas D. Reynolds, 1981, Engineering Principles of Acoustics:; Noise and Vibration Control
- Conrad J. Hemond, 1983, Engineering Acoustics & Noise Control
- F. Fahy, 2001, Foundations of Engineering Acoustics
- D.A. Biew; C.H. Hansen, 1996, Engineering Noise Control: Theory and Practice
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Central(last updated On 1/8/2026)
- Panasonic HHGTQ1001B13 LED Floor Light(last updated On 1/7/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight West | Central(last updated On 1/6/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 38
Reference 79
Hardware 55
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
