Content
Conservation of Charge
Charges of an Atom
Polarization of Atoms
Force of a Point Charge on an Atom
Source and Reference
Conservation of Charge
The net charge of a system and its surroundings cannot change. But charge can move from the systtem to surroundings or from surroundings to the system. However, charges can be created or destroyed in (+,−) pairs. For examples, electron-positron annihilation.Charges of an Atom
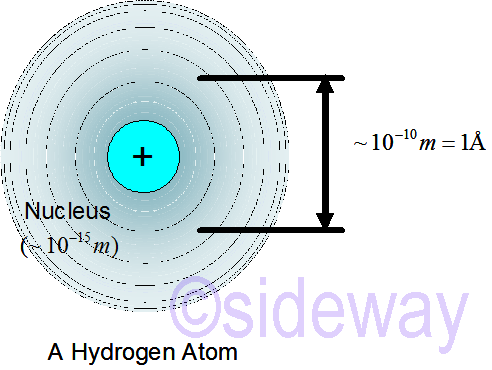 Charge of electron cloud equals that of nucleus implies neutral atom. If the electron cloud is centered on the nucleus implies electric field produced by electrons exactly cancels the field produced by nucleus.
Charge of electron cloud equals that of nucleus implies neutral atom. If the electron cloud is centered on the nucleus implies electric field produced by electrons exactly cancels the field produced by nucleus.
Polarization of Atoms
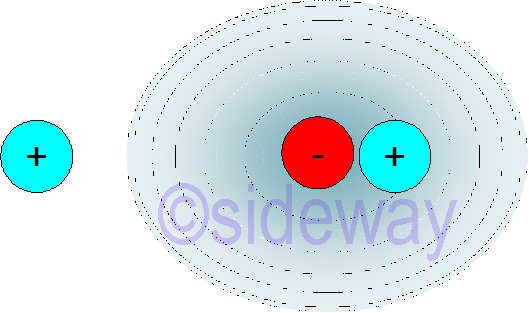 By placing a point charge close to an atom, point charge exerts electric field on the atom. Atom becomes polarized by electric field. An induced dipole can be represented as follow
By placing a point charge close to an atom, point charge exerts electric field on the atom. Atom becomes polarized by electric field. An induced dipole can be represented as follow
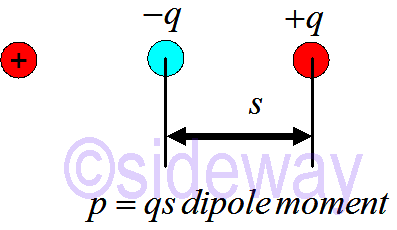 A more easily polarized atom has a larger induced dipole moment, which produces a larger electric field. And a more easily polarized atom experiences a greater attraction to a point charge.
Polarization is defined as
A more easily polarized atom has a larger induced dipole moment, which produces a larger electric field. And a more easily polarized atom experiences a greater attraction to a point charge.
Polarization is defined as
𝑝
=𝛼𝐸
where 𝛼 is polarizability of a material
|𝑝
|=𝑝=𝑞𝑠Force of a Point Charge on an Atom
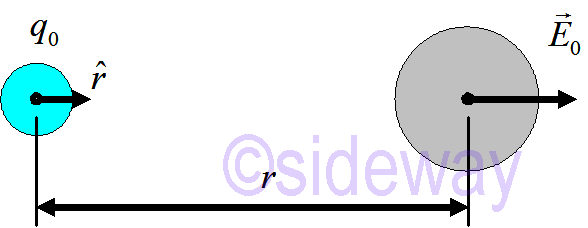 A point charge first creates electric field 𝐸0 at atom,
A point charge first creates electric field 𝐸0 at atom,
𝐸
0=14𝜋𝜀0
𝑞0𝑟2
𝑟
𝐸0 polarizes atom
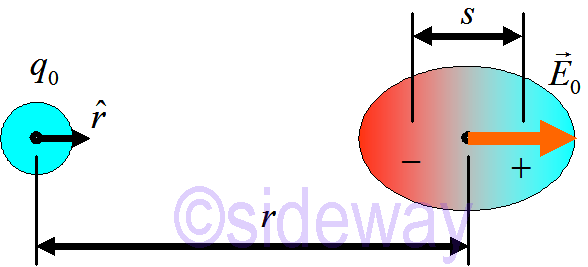 and the polarization is
and the polarization is
𝑝
=𝛼𝐸
0=14𝜋𝜀0
𝛼𝑞0𝑟2
𝑟
𝐸𝑎 at point
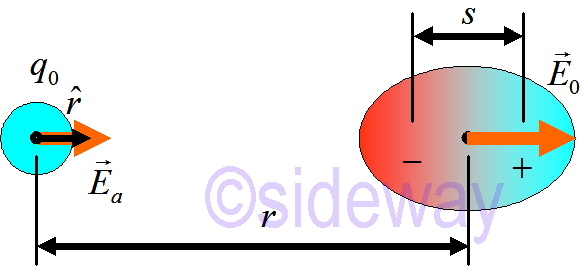 The electric field is
The electric field is
𝐸
𝑎=14𝜋𝜀0
2𝑝𝑟3
=14𝜋𝜀0
2𝛼𝐸0𝑟3
=14𝜋𝜀0
2𝛼𝑟3
14𝜋𝜀0
𝑞0𝑟2
𝑟
14𝜋𝜀0
2𝛼𝑞0𝑟5
𝑟
~1/𝑟5𝐸𝑎 due to the induced dipole exerts force on point charge
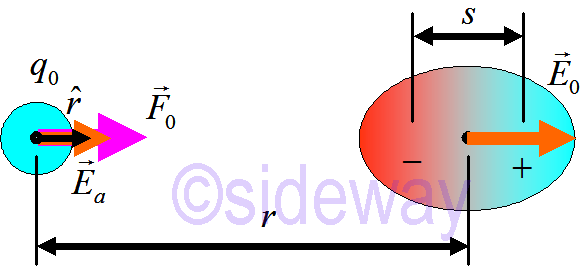 The force is
The force is
𝐹
0=𝑞0𝐸
𝑎=14𝜋𝜀0
2𝛼𝑞20𝑟5
𝑟
𝐹𝑎 that the point charge exerts on atom will be equal and opposite to the force
𝐹0
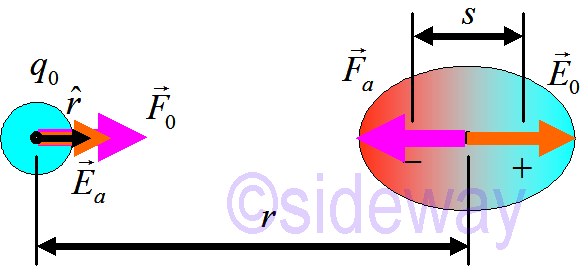 The force is
The force is
𝐹
𝑎=−𝐹
0=−𝑞0𝐸
𝑎=14𝜋𝜀0
2𝛼𝑞20𝑟5
𝑟
Source and Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rb_ybczb7Ig&list=PLZ6kagz8q0bvxaUKCe2RRvU_h7wtNNxxi&index=3
©sideway
ID: 191101002 Last Updated: 11/10/2019 Revision: 0
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Central(last updated On 1/8/2026)
- Panasonic HHGTQ1001B13 LED Floor Light(last updated On 1/7/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight West | Central(last updated On 1/6/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 38
Reference 79
Hardware 55
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
