ElectricElectric ForcePolarizationInsulatorElectric Field of Charged RodElectric Field of Charged Ring, Disk, and PlaneElectric Field of Charged Spherical ShellPotential EnergyPotential DifferenceElectric PotentialElectric EnergyElectric CurrentMagnetic FieldKirchhoff's Current LawSteady StateCapacitor Charge and DischargeRC Circuit Time ConstantCurrent Density, ConductivityMagnetic ForceElectricity, MagnetismMotor, GeneratorGauss's LawAmpere's LawFaraday's Law, Lenz's LawSuperconductor, InductorMaxwell's EquationsWave Equation
Draft for Information Only
Content
Metal and Current
Superconductor
Particles
Bose Condensation
Superconductivity
Mysteries of High Temperature Superconductors
Magnetic Flux through Superconducting ring.
Inductor
Inductance
Source and Reference
Metal and Current
Metal is shiny, smooth, malleable, carry current:conduct electricity. 𝑃=𝐼𝑉=𝐼2𝑅. Nonzero resistance. Wires radiate power away as heat. Electrons scatter off lattice, and lose energy. Reducing R is the target. Resistivity 𝜌=𝑅𝐴and lower 𝑇→smaller 𝜌→smaller power loss.
Superconductor
Superconductor have R=0. Carry current perfectly. Do not lose energy. Current in a loop will run forever. Expel magnetic fields (Meissner effect).Particles
Two kinds of particles:- Fermions: spin 1/2, 3/2, 5/2 etc. Cannot occupy the same space at the same time. Pauli exclusion principle. Antisocial.
- Bosons: spin 0, 1, 2 etc. Can occupy the same space at the same time. All follow the crowd.
Bosons can occupy the same space at the same time. Photons are bosons, e.g. lasers. Helium is a boson →superfluidity.
Bose Condensation
At low temperature, bosons flock to the lowest level. Very stable state. Dissipationless flow. superfluidity, e.g. helium. Superconductivity, most metals do this at low 𝑇.Superconductivity
Pair electrons→form bosons. Bosons condense into the lowest energy state. Lowest energy state cannot lose energy→electron pairs cannot dissipate energy. Dissipationless current flow. Lowest energy state cannot dissipate energy. That is excited atom release a photon to decrease the energy. While less excite atom release a photon to ground state. Atom in ground state cannot lose anymore energy→Quantum stability of ground state.Mysteries of High Temperature Superconductors
Brittle, Creamic, Not shiny, Not metallic Magnetic inside, make your own. How they work is still a mystery.Magnetic Flux through Superconducting ring.
Magnetic flux through superconducting ring cannot change. From Faraday's Law∮
𝐸⋅𝑑
𝑙=−
𝑑Φmag𝑑𝑡
Assume:
∮
𝐸⋅𝑑
𝑙≠0
Because 𝑅=0 in a superconductor, this would imply: 𝐼=
|emf|𝑅→∞ and is impossible. Therefore
𝑑Φmag𝑑𝑡=0 must always be true for the flux through a superconducting ring.
Inductor
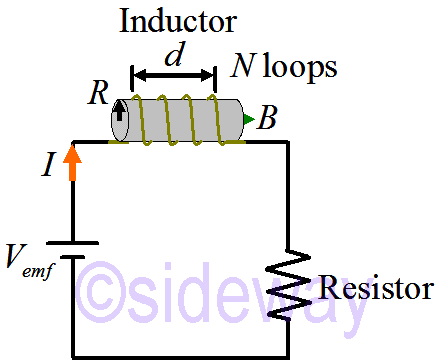 For a solenoid in steady state:𝐵=
For a solenoid in steady state:𝐵=𝜇0𝑁𝐼𝑑.
Let the current change→Induces emf in every loop:
emfloop=
=𝑑Φmag𝑑𝑡
𝑑𝑑𝑡
=𝜇0𝑁𝐼𝑑𝜋𝑅2
𝜇0𝑁𝑑𝜋𝑅2
𝑑𝐼𝑑𝑡on each loop
emftot=𝑁(emfloop)=
𝜇0𝑁2𝑑𝜋𝑅2
𝑑𝐼𝑑𝑡induced emf opposes the change
Inductance
Let inductance of solenoid 𝐿=𝑑𝐼𝑑𝑡
Because of Faraday's Law, coils of wire take awhile to reach steady state.
|emftot|=𝐼*(resistance)=𝐿
𝑑𝐼𝑑𝑡
𝐼=𝐼0[1−𝑒−(resistance*𝑡/𝐿)]=𝐼0[1−𝑒−𝑡/𝜏] where 𝜏=𝐿/(resistance)
The higher the inductance, the longer it takes to reach steady state and long time constant→inductors are used to filter out high-frequency noise.
Source and Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gKWy9FVvkHY&list=PLZ6kagz8q0bvxaUKCe2RRvU_h7wtNNxxi&index=25©sideway
ID: 200200202 Last Updated: 2/2/2020 Revision: 0
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Central(last updated On 1/8/2026)
- Panasonic HHGTQ1001B13 LED Floor Light(last updated On 1/7/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight West | Central(last updated On 1/6/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 38
Reference 79
Hardware 55
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
