Content
Kinetics:
Work, Energy, and Power
Power
Efficiency
Kinetics:
In a practical application, besides the total work done or total energy needed to do a job, sometime how fast the work is done or how fast the energy is used is a much more important concern.
Work, Energy, and Power
Work is a description of an activity that cause the displacement of an object along with the direction of force applied on. Energy is a concept of the capacity for doing work. Numerically, by the principle of work and energy, the energy processed by the object must have same value to accomplish the corresponding work. Power is defined as the time rate of doing work and therefore numerically the power of doing work has the same value as the power of the time rate of using energy to do the corresponding work.
Power
By definition, the average power of doing work is the total work done that has done during the time interval of doing the work.

By taking limit as Δt approaching zero, the instantaneous power, or the time rate of doing work at an instantaneous time interval is
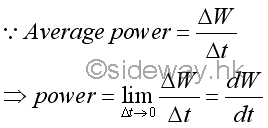
Since work done is defined as the displacement of an object in the direction of force applied on,
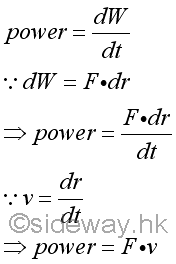
Efficiency
In practical mechanical problems, friction forces are always involved. Friction force is a non-conservative force depending on the path travelled. Since extra work is needed to overcome the work due to the friction force, the work output of a mechanical device is usually less than the work input to the mechanical device. The mechanical efficiency, b of a mechanical device is defined as the ratio of the output work over the input work to measue the efficiency of a mechanical design for a device or machine. In other words, the efficiency of a mechanical machine is always less than 1. Imply
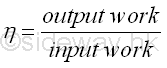
Since the derivation of the efficiency of a mechanical device or machine is based on the work that is done at a constant rate, the efficiency of a mechanical device or machine can also be expressed in term of the rates of output work done and input work done. Imply
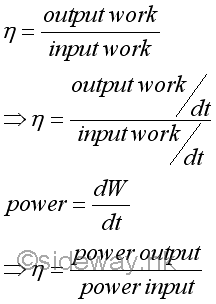
By the principle of conservation of energy, the efficiency of a device can also be applied to device transforming mechanical energy into other forms of energy such as electric energy, thermal energy etc.
©sideway
ID: 141200002 Last Updated: 12/9/2014 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- I.C. Jong; B.G. rogers, 1991, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics
- F.P. Beer; E.R. Johnston,Jr.; E.R. Eisenberg, 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Latest Updated Links
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 36W(last updated On 11/2/2025)
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 24W(last updated On 11/1/2025)
- Philips CL400 Ceiling Light 13W(last updated On 10/30/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN basket(last updated On 10/29/2025)
- Ikea TISKEN towel rack(last updated On 10/28/2025)
- Ikea REXBEGONIA mattress protector(last updated On 10/27/2025)
- Ikea KEJSAROLVON mattress protector(last updated On 10/26/2025)
- Ikea KVARNVEN ergonomic pillow(last updated On 10/25/2025)
- Ikea BRUKSVARA pocket prung mattress(last updated On 10/24/2025)
- Ikea VÅGSTRANDA pocket sprung mattress super firm(last updated On 10/23/2025)
- Ikea VITVAL underbed(last updated On 10/22/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 8
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 18
Reference 79
Hardware 25![]()
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
