Draft for Information Only
History of Intel CPU
source:
- https://timeline.intel.com/
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/company-overview/intel-museum.html
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/virtual-vault/articles/intels-founding.html last updated 14Aug2023
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/virtual-vault/articles/intels-first-product-3101.html
- https://timeline.intel.com/1969/the-1101
- https://timeline.intel.com/1970/the-intel-1103-dram
- https://timeline.intel.com/1971/the-world%27s-first-eprom:-the-1702
- https://timeline.intel.com/1971/the-first-programmable-microprocessor:-the-4004
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/museum-story-of-intel-4004.html last updated 14Aug2023
- https://timeline.intel.com/1972/establishing-the-future-of-the-microprocessor:-the-8008
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/virtual-vault/articles/the-8008.html
- https://timeline.intel.com/1974/launching-a-classic:-the-8080
- https://timeline.intel.com/1975/the-ice-80
- https://timeline.intel.com/1976/8085-microprocessor
- https://timeline.intel.com/1977/the-2716-eprom
- https://timeline.intel.com/1979/the-8088-processor
- https://timeline.intel.com/1980/do-the-math
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/virtual-vault/articles/the-8086-and-the-ibm-pc.html
- https://timeline.intel.com/1981/the-ibm-deal
- https://timeline.intel.com/1978/kicking-off-the-80286
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/articles/technical/envisioning-future-simplified-architecture.html
- https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/history/virtual-vault.html
- https://www.intel.com/pressroom/kits/quickreffam.htm
- https://www.intel-vintage.info/inteldevelopmenttools.htm
- https://www.intel-vintage.info/intelsystems.htm
- https://www.cpu-zone.com/Partnumber.htm
- https://en.wikichip.org/wiki/intel/mcs-4
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_4004
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EPROM
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8008
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8080
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_system_development_kit
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8085
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8086
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8088
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_8087
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_80186
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_80286
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intel_80386
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I386
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I486
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IBM_Personal_Computer
- https://www.nzeldes.com/HOC/IntelFirsts.htm
- http://www.cpu-collection.de/?l0=co&l1=Intel&l2=i386%20SX
- and others
| Years | Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| 1968 | Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore founded Intel to create a company that would reflect their belief in continuous innovation. |
 |
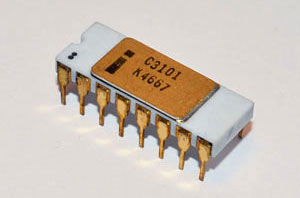
| 1969 |
The first product of Intel was SRAM, static RAM., the Intel 3101 static random-access memory.
Intel's next product, the Intel 1101 SRAM, was the first commercial chip. A calculating chip family of four chips including one pre-programmed chip for a Japanese calculator manufacturer, Busicom. |
  |
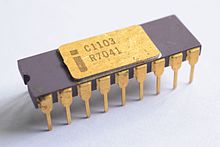
| 1970 | Intel 1103 DRAM, dynamic RAM, dynamic random-access memory was released to replace the bulky magnetic-core memories with semiconductor memories . |
 |
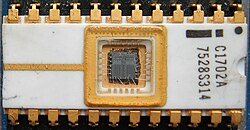
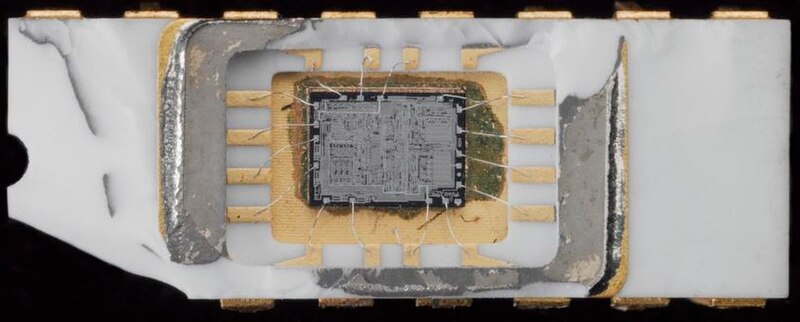
| 1971 |
The Intel 1702
EPROM, (electrically) erasable programmable read-only memory was introduced as the first EPROM for storing programs. Intel 4004 (4-bit) general-purpose programmable processor was introduced as the first electronically programmable microprocessor. The Intel 4004 central processing unit (CPU) chip together with its supporting chipset of three chips is called the MCS-4, the Micro-Computer Set-4. The chipset include an Intel 4001 read-only memory (ROM) chip for the custom applications programs, an Intel 4002 random-access memory (RAM) chip for processing data, and an Intel 4003 shift-register chip for the input/output (I/O) port. |
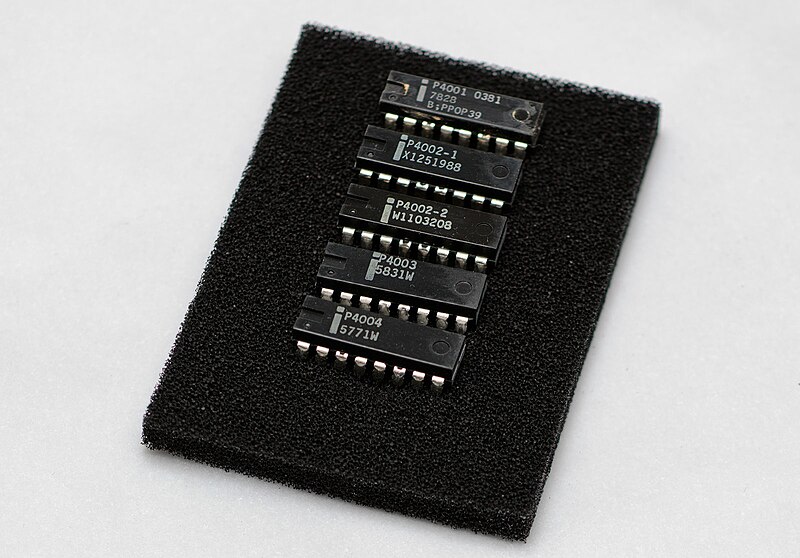   |
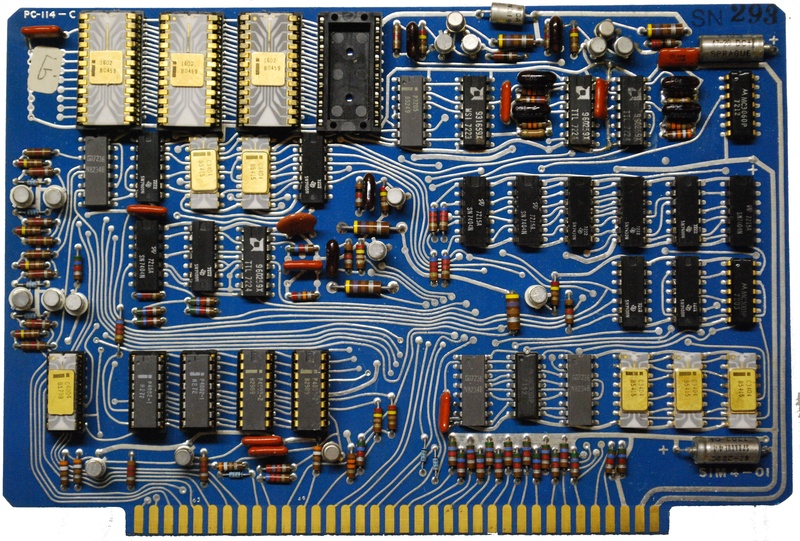
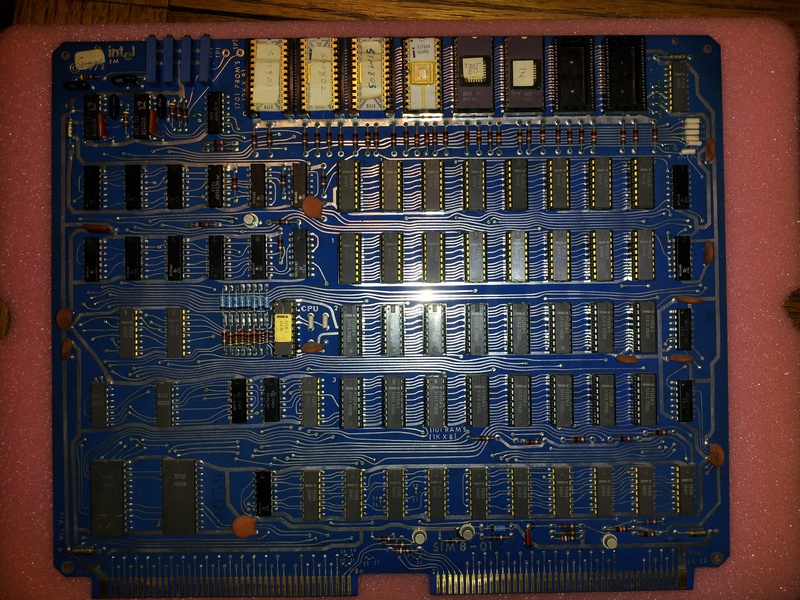
| 1972 |
The Intel 8008 (8-bit) general-purpose programmable processor was released. The SIM 4 and SIM 8 design aids were released. |
   |
| 1974 | The first Intel 8080 (8-bit) single-chip microprocessor was released. | 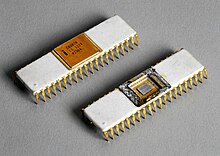 |
| 1975 |
The first Intel in-circuit emulator, ICE-80, for Intel 8080 was introduced. Intel 8080 was used to power one of the first personal computers, the Altair 8800. |
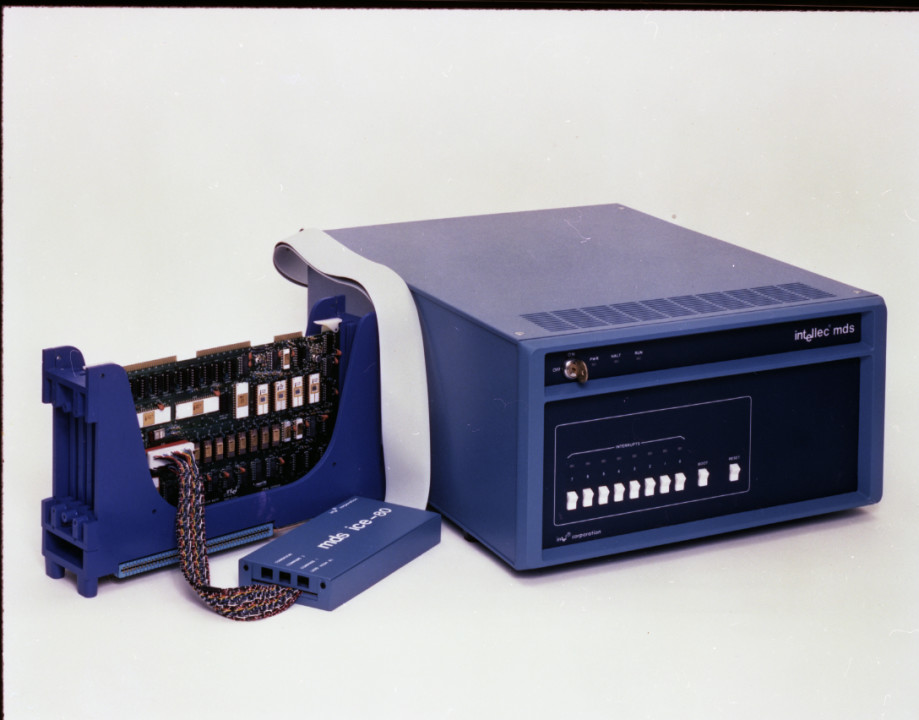  |
| 1976 |
Intel's first Single Board Computer with integrated CPU, memory and I/O peripherals, the iSBC 80/10 was released. The Intel 8085 8-bit processor using a single +5V power supply was released. |
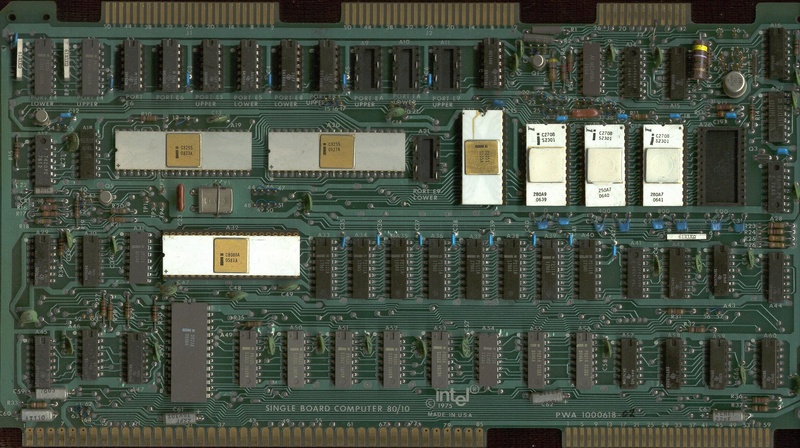  |
| 1977 | Intel 2716 16K EPROM was released. | 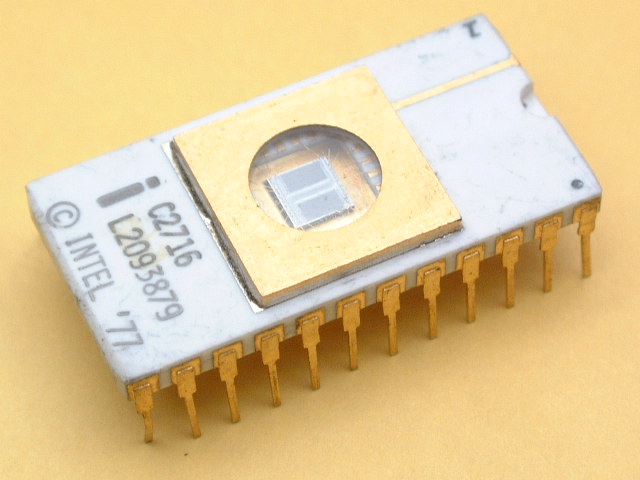 |
| 1978 | The first Intel real 16-bit 8086 microprocessor with microcode was released. |
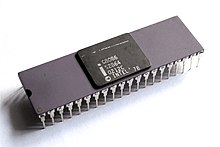 |
| 1979 | The Intel 8088 microprocessor as a variant of the Intel 8086.with eight-bit external data bus was released |
 |
| 1980 | The first Intel math coprocessor 8087 was introduced to augment the 8086 processor line. |  |
| 1981 | Intel's 16-bit 8088 was choosed by International Business Machines (IBM) as the centrol processing unit (CPU) of first mass-produced personal computer. | .png) |
| 1982 |
Intel 16-bit 80186 microprocessor (microcontroller) was released
Intel 16-bit 80286 microprocessor with multitasking support was released. |
  |
| 1985 | Intel 32-bit 80386 microprocessor was released and was renamed to i386 (80386DX) later. |   |
| 1988 | Intel 16-bit i386SX microprocessor was released. |
  |
| 1989 | Intel 32-bit i486, also known as 80486 was released. 860 960 | |
| 1990 | i750 | |
| 1991 | Touchstone Delta and Paragon | |
| 1992 | OverDrive 486 processors able to boost PC performance | |
| 1993 | Pentium processor ensured a strong future for x86 architecture | |
| 1995 | Pentium Pro | |
| 1997 | Pentium II | |
| 1998 |
Celeron microprocessor Xeon microprocessor |
|
| 1999 | Pentium III | |
| 2000 | Pentium 4 | |
| 2002 | Itanium | |
| 2003 | Mobile Pentium 4 | |
| 2005 | first multicore processor, | |
| 2006 | new logo Dual-Cores | |
| 2008 |
Core i7
Atom |
|
| 2009 | Xeon 5500 Single-Chip Cloud Computer put an entire data center 48-Core Processor | |
| 2010 | second generation Core processors | |
| 2012 | The Xeon Phi chip introduced Many Integrated Core architecture, | |
| 2013 | new Haswell architecture Core processors optimized performance for 2-in-1s | |
| 2014 | The Core M processor | |
| 2020 | 11th generation Intel Core processor | |
©sideway
ID: 230700001 Last Updated: 7/1/2025 Revision: 0
Latest Updated Links
- Pentium(last updated On 7/3/2025)
- Intel CPU(last updated On 7/2/2025)
- Intel CPU History(last updated On 7/1/2025)
- FreeGLUT Windows Function(last updated On 1/27/2025)
- FreeGLUT Initialization Function(last updated On 1/26/2025)
- FreeGLUT(last updated On 1/25/2025)
- GLUT(last updated On 1/24/2025)
- OpenGL(last updated On 1/23/2025)
- XPower UC140 4-Port 140W PD3.1 GaN Travel Charger(last updated On 1/22/2025)
- XPower DX6 6 In 1 (2x3) 60W PD3.0 Sync & Charge Cable(last updated On 1/21/2025)
- XPower MF240 1.2M Magnetic Absorption 4 in 1 (2x2) Zinc Alloy 240W PD Sync & Charge Cable(last updated On 1/20/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 8
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 18
Reference 79
Computer
Hardware 257
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
