TOCPythonLanguageCode LineCode BlockFunctionsCommon PackagesResource and LinkKnowledge BaseHow ToFAQ
LiteralString LiteralBytes LiteralInteger, Floating Point Number, Imaginary LiteralsBoolean, None LiteralsList, Tuple, Dictionary, Set, Frozenset Literals
Draft for Information Only
Content
Python Numeric Literal
Integer Literal
Definition of Integer Literal
Features of Integer
Python Integer Catalogue
Floating Point Literal
Definition of Floating Point Literal
Features of Floating Point
Python Floating Point Catalogue
Imaginary Literal
Definition of Imaginary Literal
Features of Imaginary
Source and Reference
Python Numeric Literal
Python supports numeric literals of integers, floating point numbers, and imaginary numbers. Complex literal is formed by adding a real number and an imaginary number. Besides, numeric sign is not included in numeric literal, but numeric sign '-' or '+' is considered as an unary operatorInteger Literal
An integer literal is a sequence of ASCII characters.Definition of Integer Literal
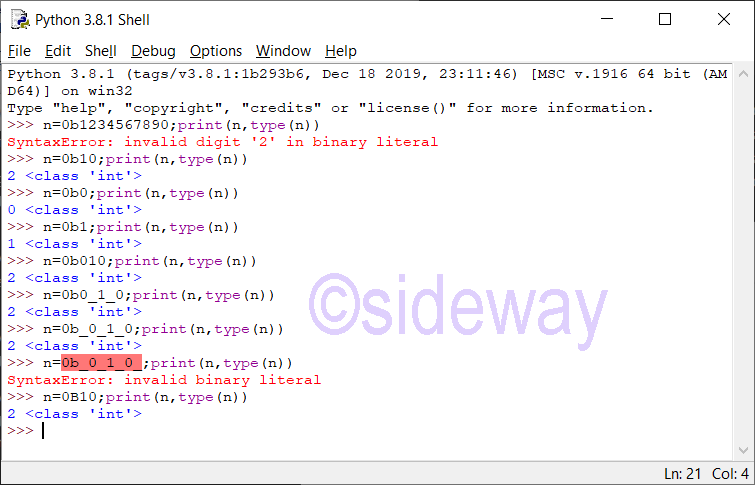
The definition of integer literal is: integer::=decinteger | bininteger | octinteger | hexinteger decinteger::=nonzerodigit (["_"] digit)* | "0"+ (["_"] "0")* bininteger::="0" ("b" | "B") (["_"] bindigit)+ octinteger::="0" ("o" | "O") (["_"] octdigit)+ hexinteger::="0" ("x" | "X") (["_"] hexdigit)+ nonzerodigit::="1"..."9" digit::="0"..."9" bindigit::="0" | "1" octdigit::="0"..."7" hexdigit::=digit | "a"..."f" | "A"..."F"Features of Integer
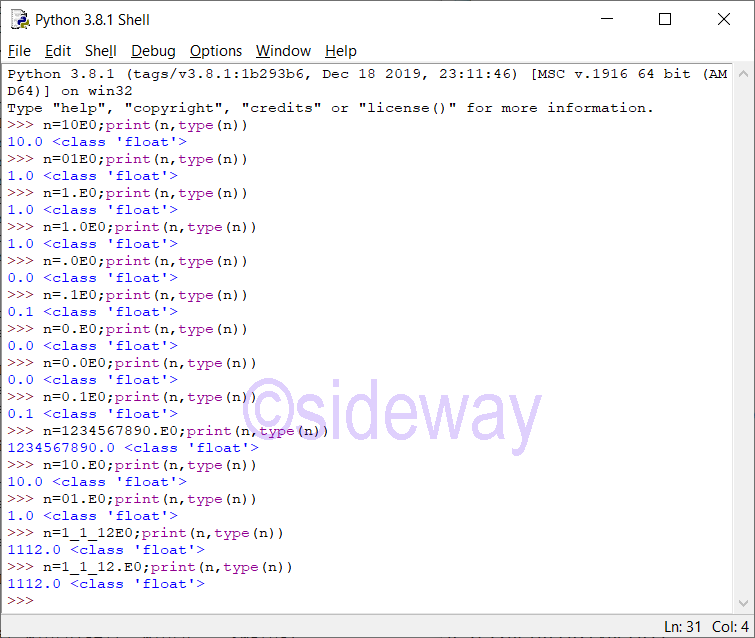
Leading zeros in a non-zero decimal number are not allowed. The length of integer literal is unlimited and is only limited by available memory. Therefore, long integer type is no longer necessary. UnderscoresPython Integer Catalogue
Python integer can be divided into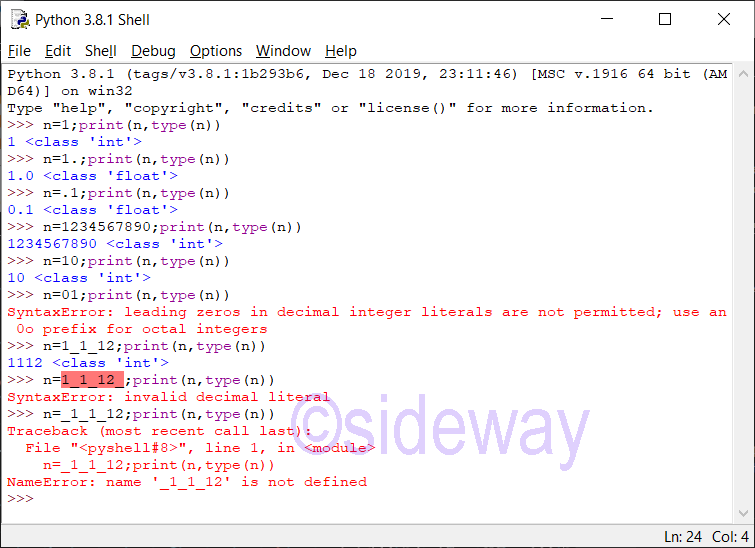
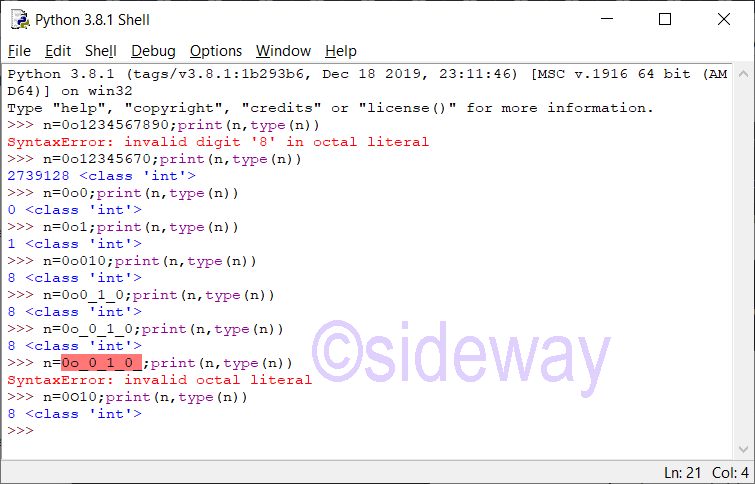
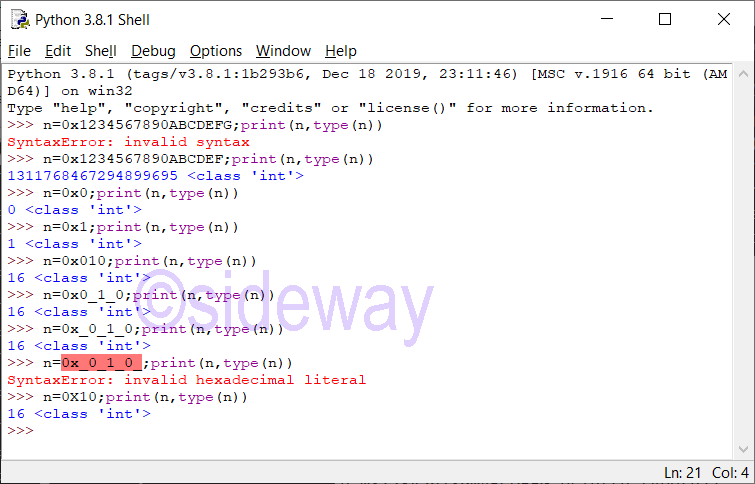
Floating Point Literal
A floating point literal is a sequence of characters for representing an floating point number with an integer part, a fractional part, and an exponent part.Definition of Floating Point Literal
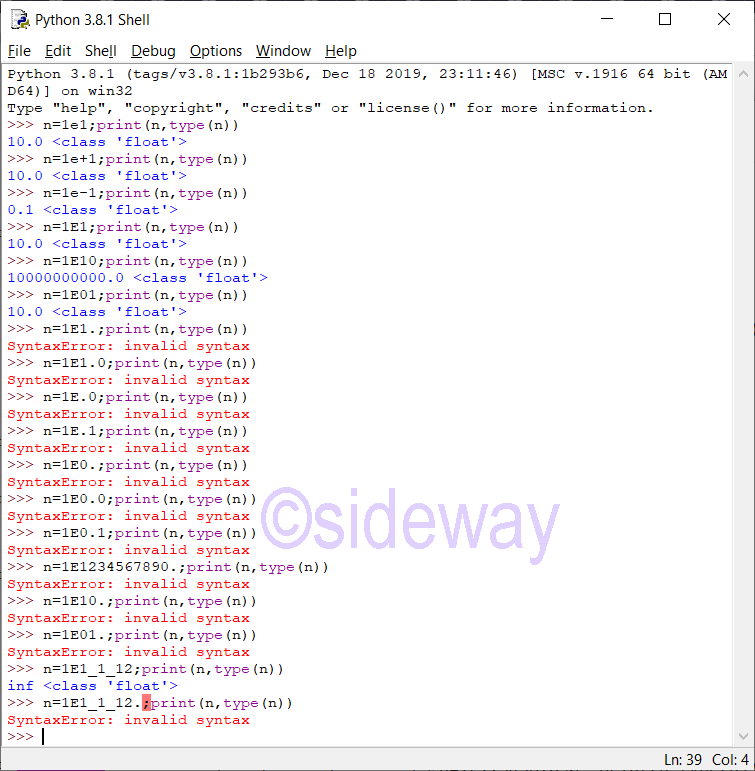
The definition of floating point literal is: floatnumber::=pointfloat | exponentfloat pointfloat::=[digitpart] fraction | digitpart "." exponentfloat::=(digitpart | pointfloat) exponent digitpart::=digit (["_"] digit)* fraction::="." digitpart exponent::=("e" | "E") ["+" | "-"] digitpartFeatures of Floating Point
Leading zeros in a floating point literal are allowed because the integer and exponent parts are always interpreted using radix 10. The allowed range of floating point literals is implementation-dependent. UnderscoresPython Floating Point Catalogue
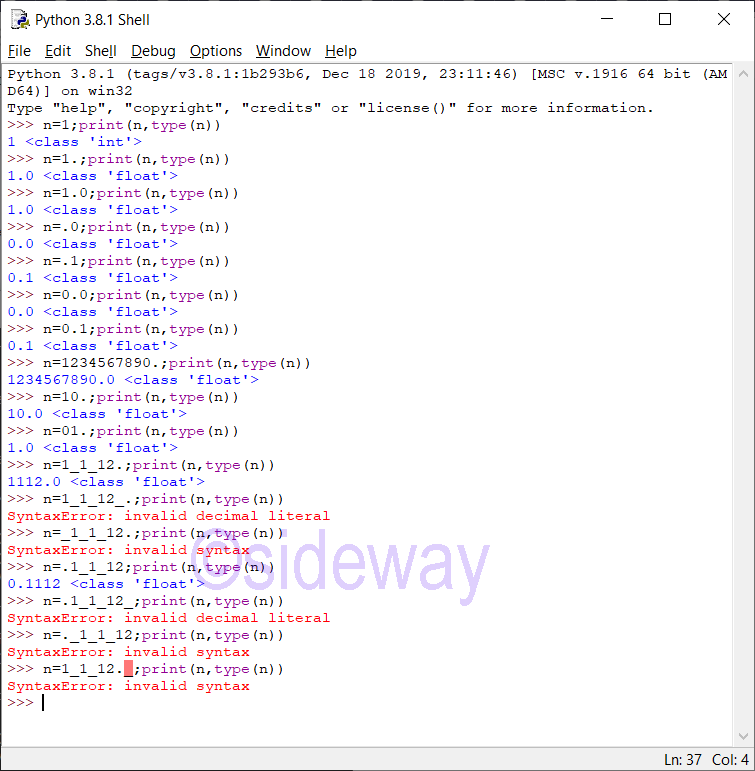
Imaginary Literal
An imaginary literal is a sequence of characters for representing an imaginary number of the imaginary part of a complex number.Definition of Imaginary Literal
The definition of imaginary literal is: imagnumber::=(floatnumber | digitpart) ("j" | "J")Features of Imaginary
An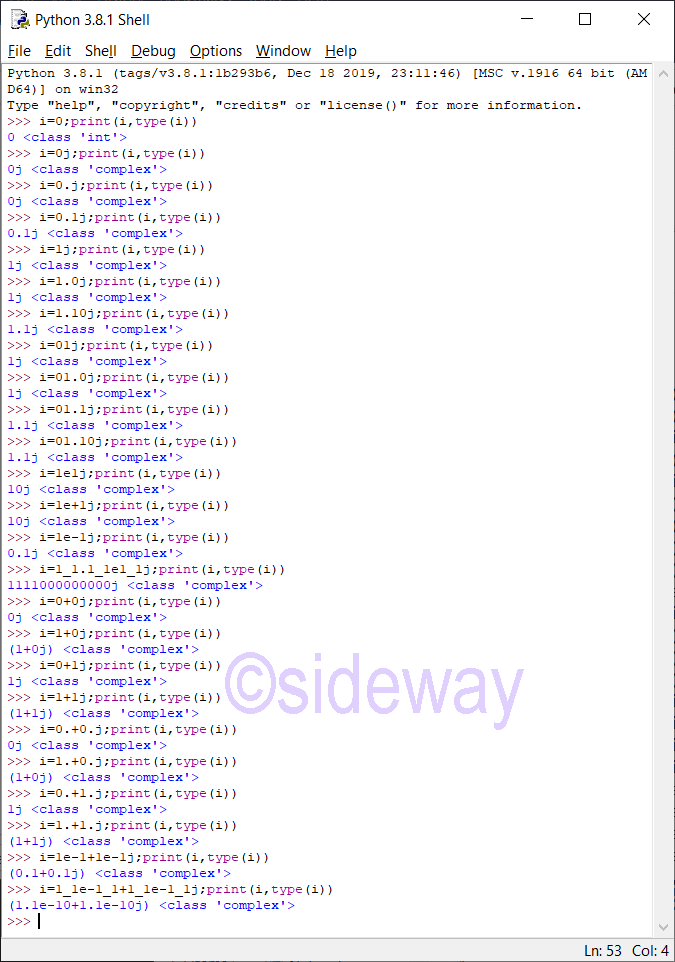
Source and Reference
- https://docs.python.org/3/reference/introduction.html
- https://docs.python.org/3/reference/lexical_analysis.html#literals
- https://docs.python.org/3/reference/expressions.html
- https://docs.python.org/2.0/ref/atom-literals.html
- https://docs.python.org/3/library/stdtypes.html#binary-sequence-types-bytes-bytearray-memoryview
©sideway
ID: 210100004 Last Updated: 1/4/2021 Revision: 0
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Space(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight AltitudeX(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight(last updated On 12/6/2025)
- Travel Singapore Rail Network(last updated On 12/5/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 31
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1