Content
Acoustic Plane Wave
Complex
Exponential Representation
Plane Wave Properties
Medium Acoustic Impedance
Plane Wave
Superimposition
Acoustic Plane Wave
For a 1D acoustic plane wave in x direction,:
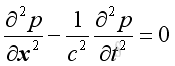
where
p is a function of
x and t.
c is the speed of propagation.
The general solution of the equation is an arbitrary wave propagation along positive x direction and negative x direction.
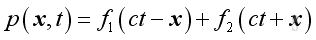
For ct-x, the propagation of pressure fluctuation should be repeated after the period ct-x, therefore after time t, the wave should propagate a distance x in positive direction outwardly.
But for ct+x, the propagation of pressure fluctuation should be repeated after the period ct+x, therefore after time t, the wave should propagate a distance x in negative direction inwardly.
Since p is a function of x and t, it is characteristic by a double periodicity.
In time domain
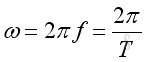
where
ω is angular velocity
ƒ is frequency
ωT is period
And in physical domain:
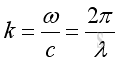
where
k is wave number
c is speed of wave propagation
λ is wave length
Consider a solution of the form:
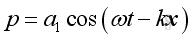
where
ω is the angular frequency
k=ω/c
a1 is the magnitude constant,
therefore:
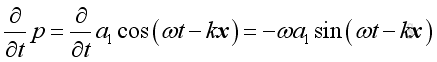 ,
,
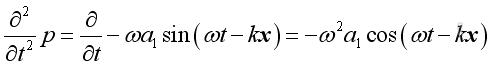
and
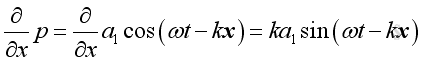 ,
,
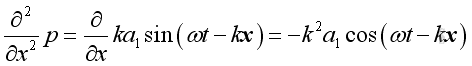
Substituting into the 1D wave equation and the form of solution is confirmed.
And a solution of the same form in negative x
direction is:
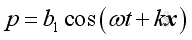
Therefore the general harmonic wave solution of wave equation is:
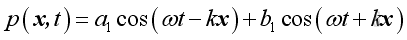
Similarly, consider a solution of the form:
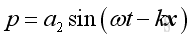
where
ω is the angular frequency
k=ω/c,
a2 is the magnitude constant,
therefore:
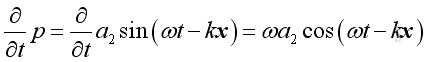 ,
,
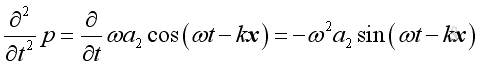
and
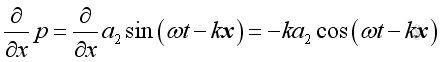 ,
,
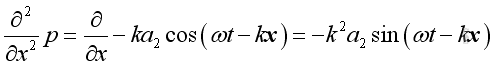
Substituting into the 1D wave equation and the form of solution is confirmed also.
Since the 1D wave equation is linearized by making the differential coefficient is of first order only, the sum of two solution forms is also a solution of the wave equation. The differences between two solutions are the phase angle and the magnitude.
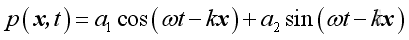
The general expression of a harmonic function is:
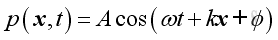
and it can be decomposed into sinusoidal and cosinusoidal components in quadrature of 90 degrees out of phase:
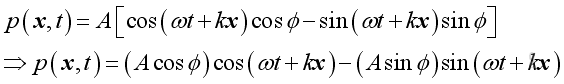
These two components can be individual harmonic function with arbitrary phase angle φ as in the first two solutions. Or they can be linked solution in a linear system in which the phase angle is not an arbitrary and is related as in the above solution:
Complex Exponential Representation
Since in complex system,
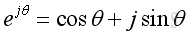
The solution of wave equation can be expressed in a complex exponential form,
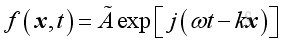
where
à is Complex function of the form
a+jb
exp[j(ωt-kx)] is
ej(ωt-kx)
j is √(-1)
Since it is a complex function, the real
acoustic pressure function can be represented by the real
part of the complex expression.
Therefore
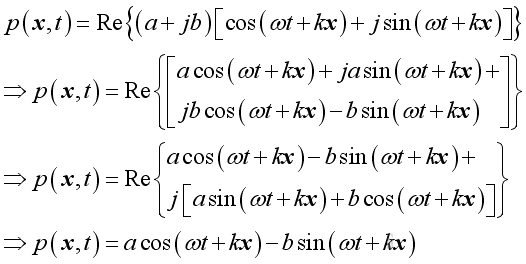
By comparing with the wave equation solution, imply:
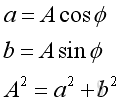
Therefore, the general complex harmonic wave solution of 1D wave equation is :
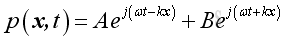
Plane Wave Properties
Consider a plane wave propagates along positive x direction:
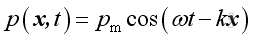 or
or
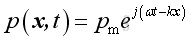
From the linearized conservation of momentum, the relationship between acoustic pressure and acoustic velocity is:
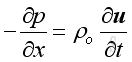
Therefore:
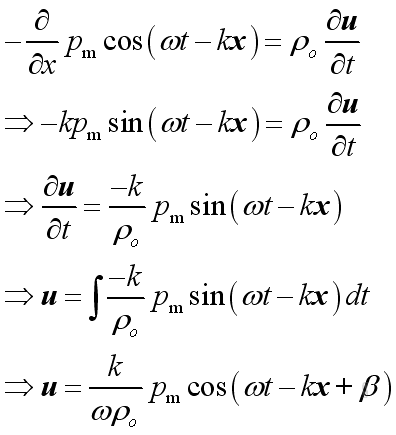
The differences in magnitude between
acoustic pressure and acoustic velocity are the relative
magnitude and the relative phase angle.
Wave propagation is a kind of forced vibration, from the linearized conservation
of momentum,
Then
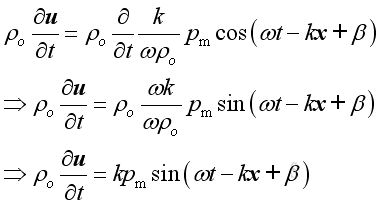 or
or
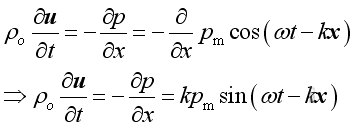
Imply :
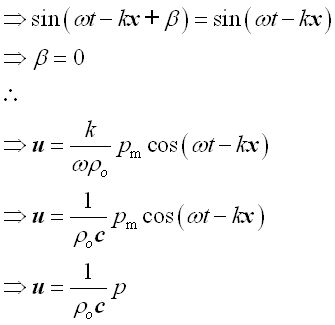
Therefore the relationship between acoustic pressure and acoustic velocity is:
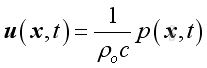
In general:
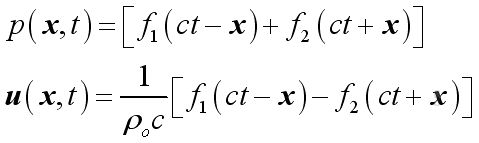
Medium Acoustic Impedance
The acoustic impedance of a medium is defined as the ratio of acoustic pressure to the acoustic velocity, Then
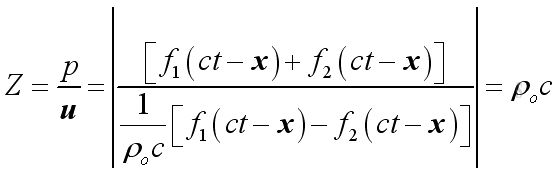
For air, z=400
Plane Wave Superimposition
Consider two harmonic plane waves propagate of the same frequency along positive x direction and negative x direction respectively. The pressure fluctuation of two harmonic plane waves i.e. A along positive x direction and B along negative x direction are
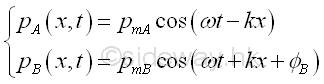
If the two harmonic plane waves are in phase at x=0, then the phase angle at x is equal to zero also. Therefore the pressure fluctuation of two harmonic plane waves at x are
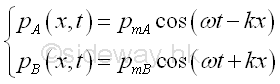
The total sound pressure at x is
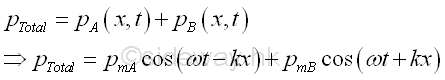
According to the linearized equation of motion,
Imply,
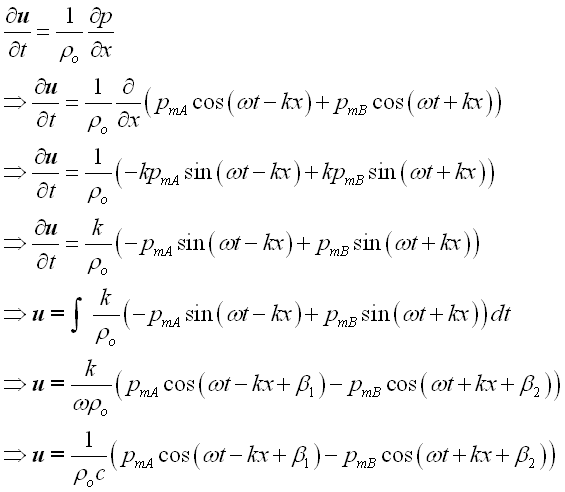
From the linearized equation of motion, imply
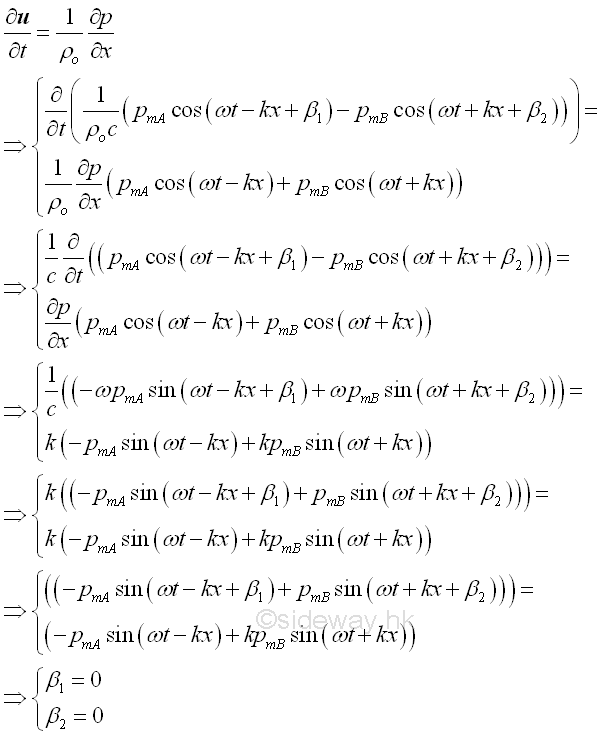
Therefore, the vector sum of the particle velocity at x is
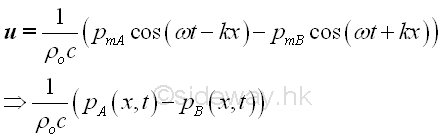
©sideway
ID: 100900021 Last Updated: 7/30/2012 Revision: 2 Ref:
References
- Michael P. Norton; Denis G. Karczub,, 2003, Fundamentals of Noise and Vibration Analysis for Engieer
- G. Porges, 1977, Applied Acoustics
- Douglas D. Reynolds, 1981, Engineering Principles of Acoustics:; Noise and Vibration Control
- Conrad J. Hemond, 1983, Engineering Acoustics & Noise Control
- F. Fahy, 2001, Foundations of Engineering Acoustics
- D.A. Biew; C.H. Hansen, 1996, Engineering Noise Control: Theory and Practice
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Space(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight AltitudeX(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight(last updated On 12/6/2025)
- Travel Singapore Rail Network(last updated On 12/5/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 31
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
