Content
Second Moment
Moment of Inertia
Second Moment
Moment is the concept of a concentrated force about a point and is proportional to the distance between the force and the reference point. In general, the first moment of a body about a reference is the summation of the moment of uniformly distributed forces over the body relating to the first order of distance and the shape of the body only. Although, the moment of distributed forces of intensity proportional to the distance between the force and the reference is also proportional to the distance between the force and the reference, the summation of the moment of the distributed forces of intensity proportional to the distance over the body relating to the square of the distance or the second order of distance and the shape of the body. Since these are common terms found in practical calculation, they are defined as the property of a body and is called the second moment of a body. For example, force acting on submerged plane surface can be expressed in terms of the differential elemental area, ΔA and the pressure, a function of the depth y, acting on the element. Imply

Since the elemental force or the distributed forces is a function the depth y, the resultant force F can be determined by making use of the first moment of the body. Similarly, since the elemental moment of the distruibuted forces about a reference is a function of the square of the depth y, the resultant moment M can be determined by making use of the second moment of the body. And the point of application y of the resultant force F can be determined through system of forces transformation by equating the moment of the two system of forces. Imply
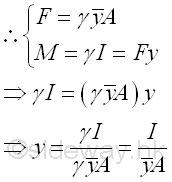
Moment of Inertia
The second moment of an area is also called moment of inertia or area moment of inertia. Besides, the application of fluid pressure of nonhorizontal submerged plane surface, second moment of an area is also involved in many engineering application analysis, e.g. bending stress, shearing stress, torsional shearing stress, angle of twist, buckling of a column, the area moment of inertia is usually refered to an plane area about an axis either parallel or normal to the plane area as the property of an plane area.
Moment of inertia is commonly used for both areas and masses. The second moment of a mass is usually used to measure a body of mass to resist changes in rotational acceleration about an axis. The tendency to resist changes in their state of motion is called as inertia. The tendency to resist rotational acceleration obtained by the second moment of a mass is therefore called the moment of inertia of the body mass about the axis or the mass moment of inertia or moment of inertia.
©sideway
ID: 121000001 Last Updated: 8/17/2013 Revision: 2 Ref:
References
- I.C. Jong; B.G. rogers, 1991, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics
- F.P. Beer; E.R. Johnston,Jr.; E.R. Eisenberg, 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Imbiah(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 36
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
