Logarithm TheoremPythagorean TheoremCombinatoricsQuadratic EquationsSequence and SeriesLinear AlgebraDiophantine EquationElliptic CurveAlgebra Result
Draft for Information Only
Content
Pythagorean Triples
Arithmetric Approach
Example 32+42=52
Example 62+82=102
General Case: 𝑐=𝑏+𝑠
Source and Reference
Pythagorean Triples
 Diophantine equation → Rational solutions.
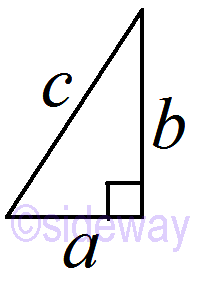
Pythagorean theorem 𝑎2+𝑏2=𝑐2
3 variables with integer solutions of Pythagorean triples.
Diophantine equation → Rational solutions.
Pythagorean theorem 𝑎2+𝑏2=𝑐2
3 variables with integer solutions of Pythagorean triples.
Arithmetric Approach
Example 32+42=52
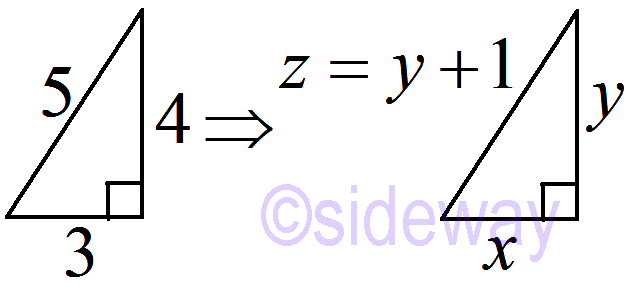 From Pythagorean theorem 𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2
From Pythagorean theorem 𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2
32+42=52⇒𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2=(𝑦+1)2
⇒𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑦2+2𝑦+1
⇒𝑥2=2𝑦+1 linear form
Since right hand side is odd, therefore 𝑥 must be odd.
Let 𝑥=2𝑘+1⇒𝑥2=(2𝑘+1)2=4𝑘2+4𝑘+1=2𝑦+1⇒2𝑘(𝑘+1)=𝑦
⇒𝑥=2𝑘+1⇒𝑦=2𝑘2+2𝑘⇒𝑧=2𝑘2+𝑘+1
Pythagorean triples {[3,4,5],[5,12,13],[7,24,25],[9,40,41],⋯}
Example 62+82=102
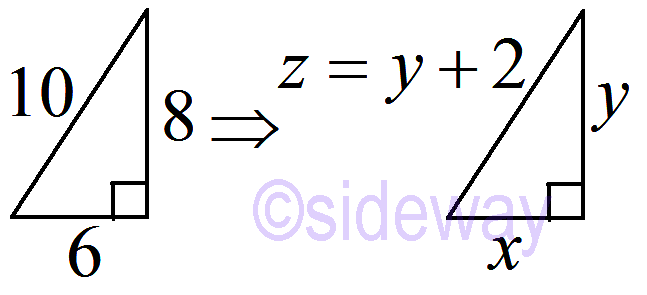 From Pythagorean theorem 𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2
From Pythagorean theorem 𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2
62+82=102⇒𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2=(𝑦+2)2
⇒𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑦2+4𝑦+4
⇒𝑥2=4𝑦+4=4(𝑦+1) linear form
Since right hand side is even, therefore 𝑥 must be even.
Let 𝑥=2𝑙⇒𝑥2=(2𝑙)2=4𝑙2=4(𝑦+1)⇒𝑙2−1=𝑦
let 𝑙=𝑘,
⇒𝑥=2𝑘⇒𝑦=𝑘2−1⇒𝑧=𝑘2+1
Pythagorean triples {[4,3,5],[6,8,10],[8,15,17],[10,24,26],⋯}
General Case: 𝑐=𝑏+𝑠
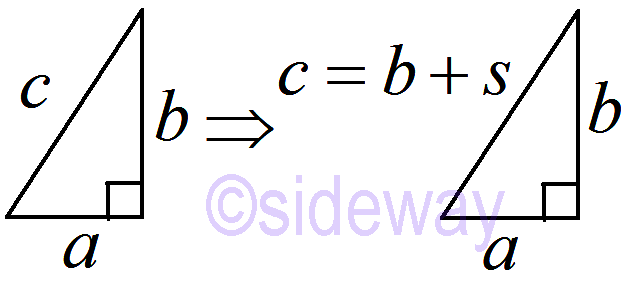 Goal: {𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2}={𝑥=𝑥(param),𝑦=𝑦(param),𝑧=𝑧(param)}
Goal: {𝑥2+𝑦2=𝑧2}={𝑥=𝑥(param),𝑦=𝑦(param),𝑧=𝑧(param)}cases and reduction: primitive solutions if
Let 𝑃(𝑥0,𝑦0,𝑧0) be a primitive solution.
Let 𝑧0=𝑦0+𝑠, 𝑠∊ℤ
𝑥20+𝑦20=𝑧20
⇒𝑥20+𝑦20=(𝑦0+𝑠)2
⇒𝑥20+𝑦20=𝑦20+2𝑠𝑦0+𝑠2
⇒𝑥20=2𝑠𝑦0+𝑠2
Let 𝑥0=𝑡
⇒𝑡2=2𝑠𝑦0+𝑠2
⇒𝑦0=𝑡2−𝑠22𝑠
⇒𝑧0=𝑦0+𝑠=𝑡2+𝑠22𝑠
⇒𝑥20+𝑦20=𝑧20⇒(𝑡)2+𝑡2−𝑠22𝑠
𝑡2+𝑠22𝑠
Check
- Is ther an odd common prime factor 𝑝? Let 𝑝|𝑚 and 𝑝|𝑦2⇒𝑝|𝑛⇒contradict to
gcd(𝑚,𝑛)=1 - test an even factor by
Mod2𝑚20011 𝑛20101 𝑚2−𝑛20110 𝑚2+𝑛20110Case both 𝑚2 and 𝑛2 are even⇒contradict togcd(𝑚,𝑛)=1
Case either 𝑚2 or 𝑛2 are even⇒no factor of 2 and 𝑚≢𝑛Mod2⇒(𝑥2,𝑦2,𝑧2) is primitive.
Case both 𝑚2 and 𝑛2 are odd, 𝑚≡𝑛≡1Mod2.⇒𝑥2=2𝑚𝑛,𝑦2=𝑚2−𝑛2,𝑧2=𝑚2+𝑛2 are even.
Let 𝑚+𝑛=2𝐴; 𝑚−𝑛=2𝐵⇒𝑚=(𝐴+𝐵); 𝑛=(𝐴−𝐵)
⇒𝑥2=2𝑚𝑛=2(𝐴+𝐵)(𝐴−𝐵)=2(𝐴2−𝐵2)
⇒𝑦2=𝑚2−𝑛2=(𝑚+𝑛)(𝑚−𝑛)=(2𝐴)(2𝐵)=4𝐴𝐵
⇒𝑧2=𝑚2+𝑛2=(𝐴+𝐵)2+(𝐴−𝐵)2=(𝐴2+2𝐴𝐵+𝐵2)+(𝐴2−2𝐴𝐵+𝐵2)=2(𝐴2+𝐵2)
2 is the common factor
⇒𝑥3=𝐴2−𝐵2
⇒𝑦3=2𝐴𝐵
⇒𝑧2=𝐴2+𝐵2
If both 𝐴 and 𝐵 are odd, then the conversion can be repeated since 𝑃(𝑥,𝑦,𝑧) are always of the same form with the two terms on the left hand side are changed alternatively when 2 is the common factor of 𝑃(𝑥,𝑦,𝑧). When there is no more even common factor for 𝑃(𝑥,𝑦,𝑧),gcd(𝐴,𝐵)=1 or (𝑥,𝑦,𝑧) is primitive, and 𝐴 and 𝐵 can only be in opposite parity.
𝑥0=2𝑢𝑣
𝑦0=𝑢2−𝑣2
𝑧0=𝑢2+𝑣2
where gcd(𝑢,𝑣)=1 and 𝑢≢𝑣 Mod 2
Source and Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bTenb0VPa3Ahttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4D9ttfBNIJI
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eRXWpWgP0dQ
©sideway
ID: 201100014 Last Updated: 11/14/2020 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- B. Joseph, 1978, University Mathematics: A Textbook for Students of Science & Engineering
- Wheatstone, C., 1854, On the Formation of Powers from Arithmetical Progressions
- Stroud, K.A., 2001, Engineering Mathematics
- Coolidge, J.L., 1949, The Story of The Binomial Theorem
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/10/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight(last updated On 12/6/2025)
- Travel Singapore Rail Network(last updated On 12/5/2025)
- Travel Singapore Things to Know(last updated On 12/4/2025)
- Travel Singapore(last updated On 12/3/2025)
- Legrand Galion(last updated On 12/2/2025)
- Schneider Electric AvatarOn(last updated On 12/1/2025)
- Alfalux(last updated On 11/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 26![]()
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
