Logarithm TheoremPythagorean TheoremCombinatoricsQuadratic EquationsSequence and SeriesLinear AlgebraDiophantine EquationElliptic CurveAlgebra Result
Draft for Information Only
Content
Pythagorean Triples
Geometric Approach
𝑦-intercept
Conic Section Example 𝑥2+2𝑦2=1
Key Ingredients for Binary Operation: 𝑥2+𝑑𝑦2=1
Generalization to degree 3 with three variables
Generalization to twists: 𝑎𝑥2+𝑏𝑦2=𝑐→𝑥2+𝑎𝑦2=𝑏
Key Ingredients for Parameterisation: 𝑥2+𝑑𝑦2=1
Source and Reference
Pythagorean Triples
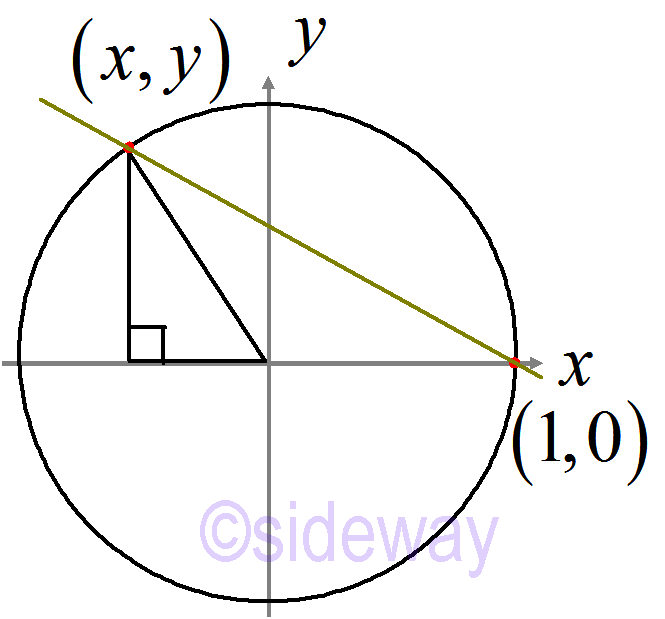 Pythagorean triples: 𝑥2+𝑦2=1 with rational solutions. The rational solution (𝑥,𝑦) can also be reference to another fixed rational point i.e. (1,0)
Pythagorean triples: 𝑥2+𝑦2=1 with rational solutions. The rational solution (𝑥,𝑦) can also be reference to another fixed rational point i.e. (1,0)
Geometric Approach
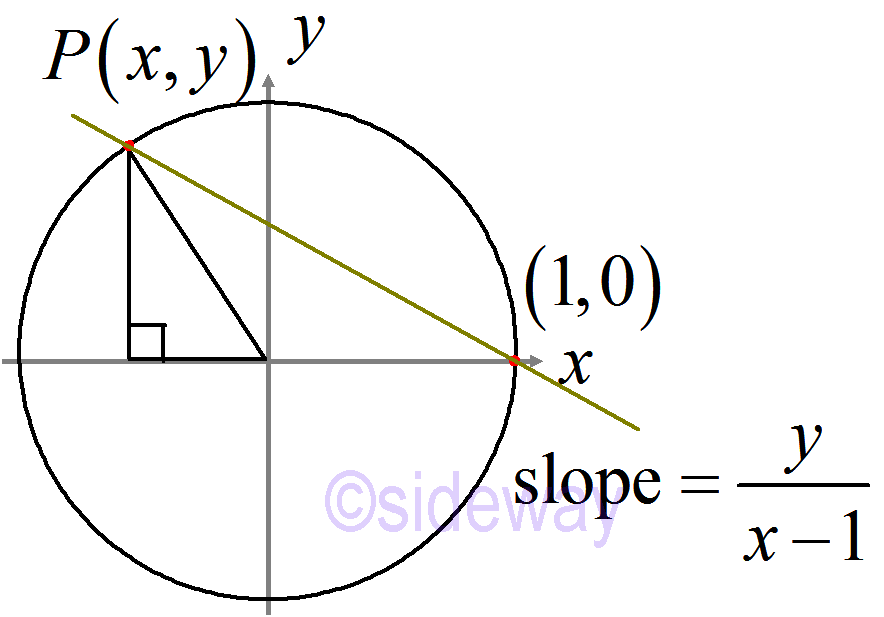 By sweeping a line about a fixed rational point (1,0), the slope of the line jointing the rational point (𝑥,𝑦) can be used to represent this rational point. And the slope is equal to
By sweeping a line about a fixed rational point (1,0), the slope of the line jointing the rational point (𝑥,𝑦) can be used to represent this rational point. And the slope is equal to 𝑦𝑥−1. Since the rational solutions of 𝑥2+𝑦2=1 always preserves the rationality of slope. In other words, the rational point (𝑥,𝑦) is mapped to a rational slope.
𝑍0={(𝑥,𝑦):𝑥2+𝑦2=1,𝑥≠1}
𝑚:𝑍0→ℚ given by 𝑚(𝑃)=𝑦𝑥−1
Similarly, the map 𝑚 can be defined for more general curves. And the properties of 𝑚 are
- 𝑚 is 1-to-1
- 𝑚 is surjective.
- 𝑚−1:ℚ→𝑍0 is given by rational functions
𝑦-intercept
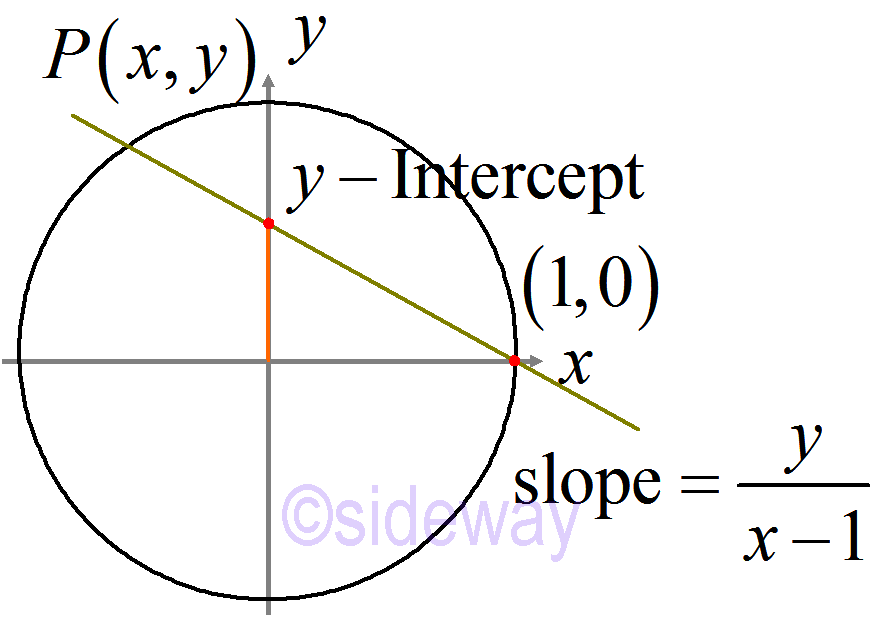 Similar to Riemann stereographic projection, the slope of the sweeping line can be projected as the 𝑦-intercept on the 𝑦-axis. The parameterisation of the 2-degee equation with one fixed point gives one unique association with the remaining point.
Let 𝑚−1(𝑡)=(𝑥,𝑦); 𝑥2+𝑦2=1
⇒𝑚(𝑃)=𝑡⇒
Similar to Riemann stereographic projection, the slope of the sweeping line can be projected as the 𝑦-intercept on the 𝑦-axis. The parameterisation of the 2-degee equation with one fixed point gives one unique association with the remaining point.
Let 𝑚−1(𝑡)=(𝑥,𝑦); 𝑥2+𝑦2=1
⇒𝑚(𝑃)=𝑡⇒𝑦𝑥−1=𝑡 ⇒𝑦=𝑡(𝑥−1) and 𝑥2+𝑦2=1 Let 𝑧=𝑥−1 ⇒𝑦=𝑡𝑧 and (𝑧+1)2+𝑦2=1 ⇒(𝑧+1)2+(𝑡𝑧)2=1 ⇒𝑧2+2𝑧+𝑡2𝑧2=0 ⇒(1+𝑡2)𝑧2+2𝑧=0 If 𝑧≠0 ⇒(1+𝑡2)𝑧+𝑧=0 ⇒𝑧=−
21+𝑡2⇒𝑥−1=−
21+𝑡2⇒𝑥=
𝑡2−11+𝑡2∊ℚ ⇒𝑦=𝑡𝑧=𝑡
21+𝑡2
2𝑡1+𝑡2⇒𝑚−1(𝑡)=(𝑥,𝑦)=
𝑡2−11+𝑡2,−
2𝑡1+𝑡2
Conic Section Example 𝑥2+2𝑦2=1
Similar to other conic section.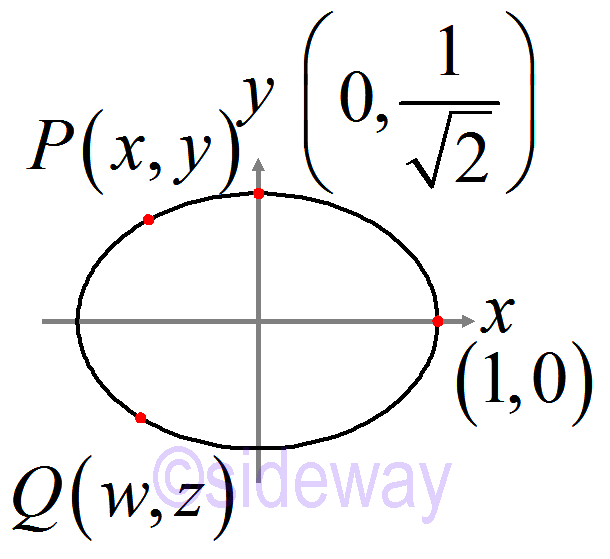 Binary Operation of 𝑥2+2𝑦2=1
Binary Operation of 𝑥2+2𝑦2=1Let 𝑃(𝑥,𝑦),𝑄(𝑤,𝑧) be the solution of the equation. ⇒(𝑥+𝑦√2𝑖)(𝑥−𝑦√2𝑖)=1 and (𝑤+𝑧√2𝑖)(𝑤−𝑧√2𝑖)=1 ⇒(𝑥𝑧−2𝑦𝑤)2+2(𝑥𝑤+𝑦𝑧)2=1 So 𝑃⊕𝑄=𝑅 where 𝑅=(𝑥𝑧−2𝑦𝑤,𝑥𝑤+𝑦𝑧)
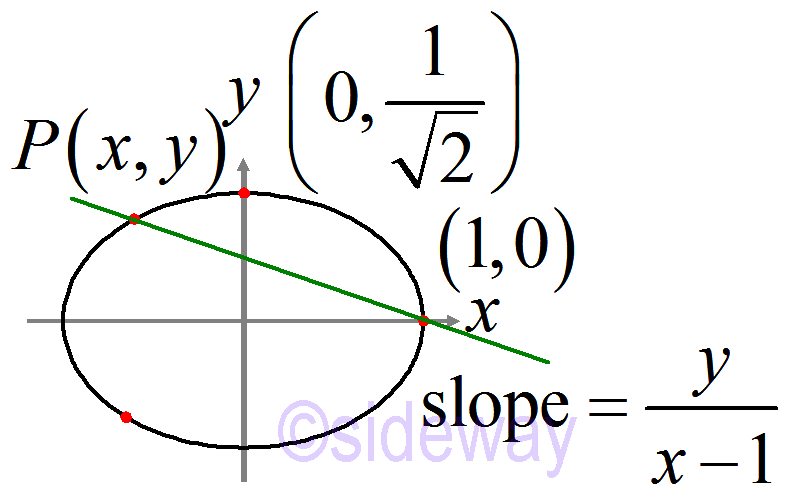 map 𝑚:𝑍0→ℚ given by 𝑚(𝑃)=
map 𝑚:𝑍0→ℚ given by 𝑚(𝑃)=𝑦𝑥−1where 𝑍0={(𝑥,𝑦):𝑥2+2𝑦2=1, 𝑥≠1} 𝑚−1(𝑡)=(𝑥,𝑦), where 𝑦=𝑡(𝑥−1) Let 𝑧=𝑥−1⇒(𝑧+1)2+2𝑡2𝑧2=1⇒𝑧((1+2𝑡2)𝑧+2)=0 ⇒𝑧=−2/(1+2𝑡2) ⇒𝑥=
2𝑡2−11+2𝑡2⇒𝑦=
−2𝑡21+2𝑡2⇒𝑚−1(𝑡)=
2𝑡2−11+2𝑡2,
−2𝑡21+2𝑡2
Key Ingredients for Binary Operation: 𝑥2+𝑑𝑦2=1
𝑥2+𝑑𝑦2=1- RHS being 1
- (𝑥+𝑦√𝑑)𝑛=𝑥'+𝑦'√𝑑⇒𝑥2𝑛+𝑑𝑦2𝑛=1
Generalization to degree 3 with three variables
𝑥3+2𝑦3−6𝑥𝑦𝑧+4𝑧3=1⇒manipulate ∛2Generalization to twists: 𝑎𝑥2+𝑏𝑦2=𝑐→𝑥2+𝑎𝑦2=𝑏
Key Ingredients for Parameterisation: 𝑥2+𝑑𝑦2=1
- A rational point (1,0)
- The degree being 2⇒𝑚−1:ℚ→𝑍0
Source and Reference
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XiwGK8sdwpQhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eLoQz1WRFu0
©sideway
ID: 201100016 Last Updated: 11/16/2020 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- B. Joseph, 1978, University Mathematics: A Textbook for Students of Science & Engineering
- Wheatstone, C., 1854, On the Formation of Powers from Arithmetical Progressions
- Stroud, K.A., 2001, Engineering Mathematics
- Coolidge, J.L., 1949, The Story of The Binomial Theorem
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight AltitudeX(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Space(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Curiosity Cove(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Night Safari(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight River Wonders(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 33
Reference 79
Hardware 54
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
