Content
Moment of Inertia of Composite Body
Moment of Inertia of a
Mass of Homogeneous Composite Body
Moment of Inertia of
Hollow Circular Cylinder
Moment of Inertia of Hollow Sphere
Radius of Gyration of Composite Body
Moment of Inertia of Composite Body
By definition, moment of inertia about an axis is equal to the summation of the products of the square of the distance between the elemental mass and the reference axis, and the elemental mass over the body. If these elemental mass can be grouped into known component masses M1, M2, M3, ...., the second moment I of the composite body A with respect to an axis can be obtained by the summation of the second moments, I1, I2, I3, .... of these component masses M1, M2, M3, ...., about the same reference axis respectively. Imply
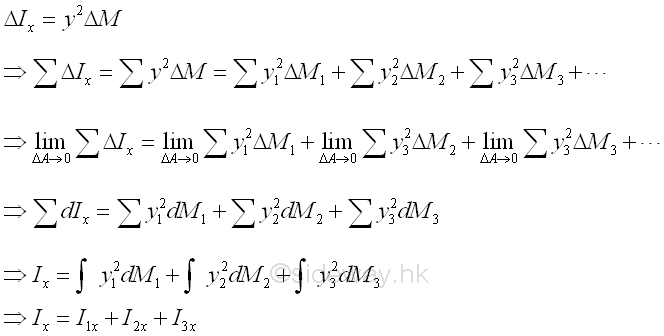
The component body of a composite body is represented by a positive mass while a hollow body is represented by a negative mass.
Moment of Inertia of a Mass of Homogeneous Composite Body
Moment of Inertia of Hollow Circular Cylinder
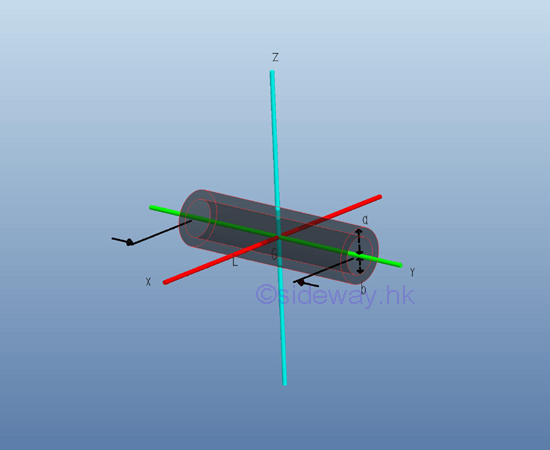
Consider a homogenous hollow circular cylinder of length L with uniform cross-sectional area A of inner radius b, outer radius a and homogenouse material density l. Both the cross-sectional area and the material density are constant over the lenght, the mass and the elemental mass of the hollow circular cylinder can be expressed in terms of the volume of the hollow circular cylinder. Since the cross-sectional radius cannot be neglected, the actual distance between the elemental mass and the reference axis should be used. The moments of inertia about axes x and z, can be determined by the method of composite body. Imply
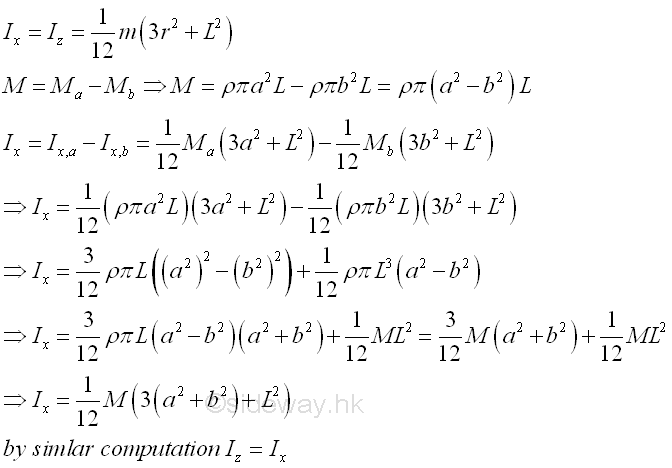
And the moments of inertia about axis y can also be determined by parallel-axis theorem. Imply
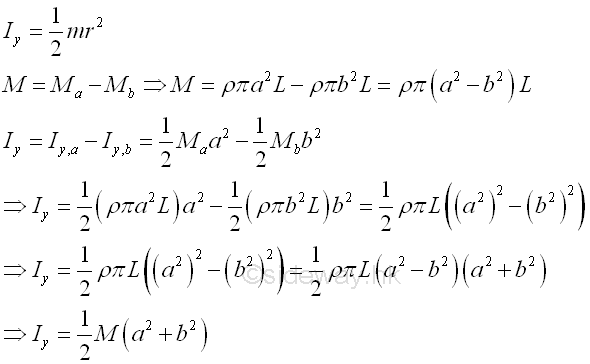
Moment of Inertia of Hollow Sphere
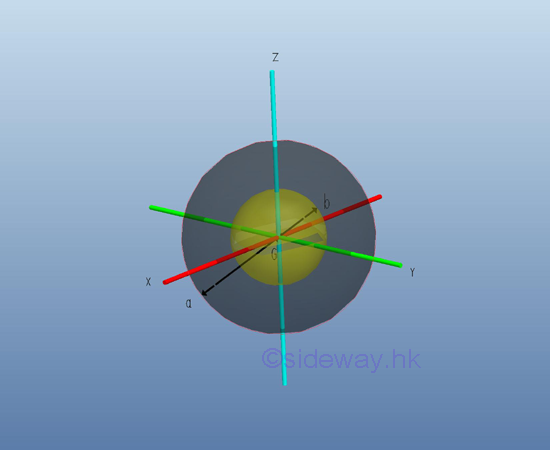
Consider a homogenous hollow sphere of inner radius b, outer radius a and homogenouse material density l. The material density are constant over the lenght, the mass and the elemental mass of the hollow sphere can be expressed in terms of the volume of the hollow sphere. Since the cross-sectional radii cannot be neglected, the actual distance between the elemental mass and the reference axis should be used. The moments of inertia about axes x, y, and z, can be determined by the method of composite body. Imply
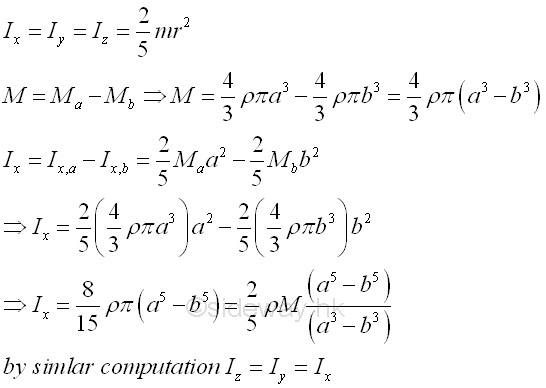
Radius of Gyration of Composite Body
Similar to case of the area moment of inertia, the radius of gyration of a composite body can not be obtained using the radii of gyration of all component bodies of a composite body only. The radius of gyration of a composite body can be determined by the second moment of the composite body and the mass of the composite body directly or making use of the radii of gyration of all component bodies of a composite body together with the masses of the component bodyies of a composite body. Imply
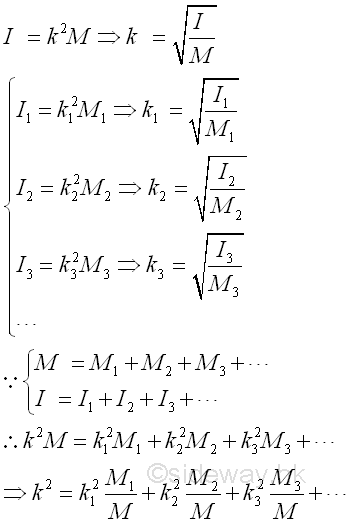
©sideway
ID: 121100087 Last Updated: 11/16/2012 Revision: 0 Ref:
References
- I.C. Jong; B.G. rogers, 1991, Engineering Mechanics: Statics and Dynamics
- F.P. Beer; E.R. Johnston,Jr.; E.R. Eisenberg, 2004, Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics
Latest Updated Links
- Travel Singapore Sight Central(last updated On 1/8/2026)
- Panasonic HHGTQ1001B13 LED Floor Light(last updated On 1/7/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight West | Central(last updated On 1/6/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Sensoryscape(last updated On 1/5/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa Resorts World Sentosa(last updated On 1/4/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa HarbourFront(last updated On 1/3/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Sentosa(last updated On 1/2/2026)
- Travel Singapore Sight Bird Paradise(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Mandai(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Singapore Zoo(last updated On 12/30/2025)
- Travel Singapore Sight Rainforest Wild ASIA(last updated On 12/30/2025)

 Nu Html Checker
Nu Html Checker  53
53  na
na  na
na
Home 5
Business
Management
HBR 3
Information
Recreation
Hobbies 9
Culture
Chinese 1097
English 339
Travel 38
Reference 79
Hardware 55
Computer
Hardware 259
Software
Application 213
Digitization 37
Latex 52
Manim 205
KB 1
Numeric 19
Programming
Web 289
Unicode 504
HTML 66
CSS 65
SVG 46
ASP.NET 270
OS 431
DeskTop 7
Python 72
Knowledge
Mathematics
Formulas 8
Set 1
Logic 1
Algebra 84
Number Theory 206
Trigonometry 31
Geometry 34
Calculus 67
Engineering
Tables 8
Mechanical
Rigid Bodies
Statics 92
Dynamics 37
Fluid 5
Control
Acoustics 19
Natural Sciences
Matter 1
Electric 27
Biology 1
